Figures & data
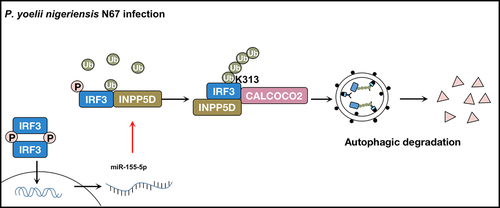
Figure 1. A proposed working model to illustrate the negative feedback loop of IFN-I signaling generated by IRF3-miR-155-INPP5D-CALCOCO2 axis in anti-malarial immunity. During P. yoelii nigeriensis N67 infection, INPP5D interacts with phosphorylated IRF3 and enhances K63-linked poly-ubiquitination of IRF3 at K313, thereby stabilizing the interaction between IRF3 and its selective autophagy receptor CALCOCO2. Binding between INPP5D, IRF3, and CALCOCO2 strengthens the autophagic degradation of activated IRF3, depleting IFN-I responses against P. yoelii infection. Additionally, IRF3-dependent IFN-I response activated by P. yoelii gDNA and RNA induces miR-155-5p expression to downregulate INPP5D, acting as a negative feedback loop between IFN-I signaling and autophagy.