Figures & data
Table 1 Demographic characterization of patients with pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants in FTLD-associated genes at UCSF and commercial clinical laboratory
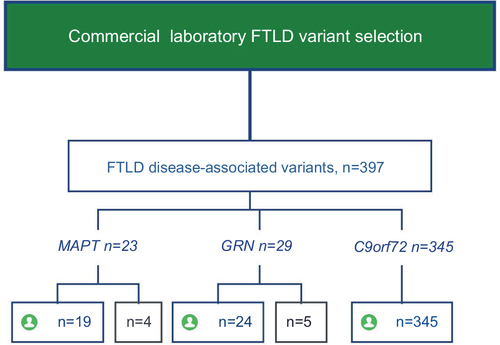
Figure 1 GRN variants in cohorts from UCSF and a Commercial Clinical Laboratory.
Abbreviation: UCSF, University of California, San Francisco.
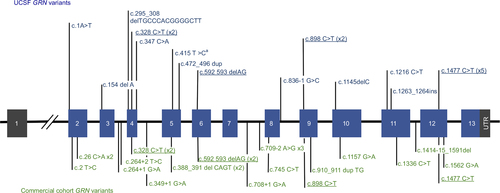
Figure 2 Neuroimaging from select GRN variant cases.
Abbreviations: CDR, clinical dementia rating; R, right; L, left.
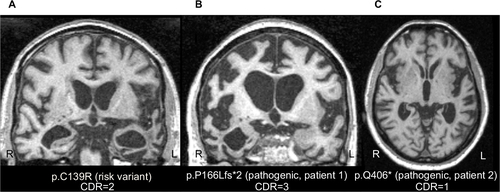
Table S1 Transcript IDs
Table S2 GRN variants included in this study; count in the commercial clinical laboratory/UCSF cohort and overall ExAC frequenciesa
Table S3 Pathogenic/likely pathogenic MAPT variants included in this study; count in commercial clinical laboratory/UCSF cohort and overall ExAC frequenciesa
Table S4 Type and quantity of overlap in MAPT and GRN variants between cohorts from UCSF and a commercial clinical laboratory
Figure S1 Selection of participants from UCSF.
Abbreviations: UCSF, University of California, San Francisco; FTLD, frontotemporal lobar degeneration.
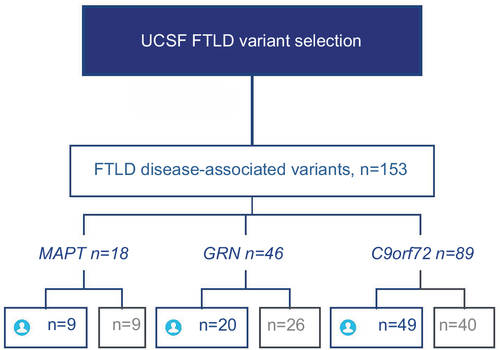
Figure S2 Selection of participants from a commercial clinical laboratory.
Abbreviation: FTLD, frontotemporal lobar degeneration.