Figures & data
Table 1 Selected Characteristics of the Study Population
Table 2 Prediction Model for the Risk of 1-Year Risk of Intracranial Bleeding
Figure 2 Observed vs. predicted ICH events based on AF ICH risk model.
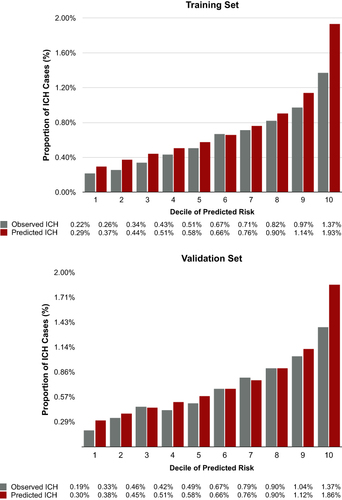
Table 3 Comparison Between Recalibrated HAS-BLED Score and Homer Score vs. New ICH Model: Reclassification of Predicted 1-Year ICH Risk Categories in the Validation Set
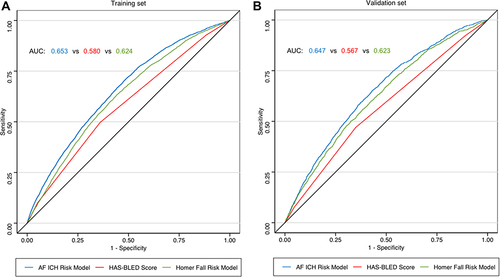
Figure 3 Comparison of AF ICH risk model vs. HAS-BLED score and vs. Homer fall risk model: AUC in predicting 1-year risk of ICH.