Figures & data
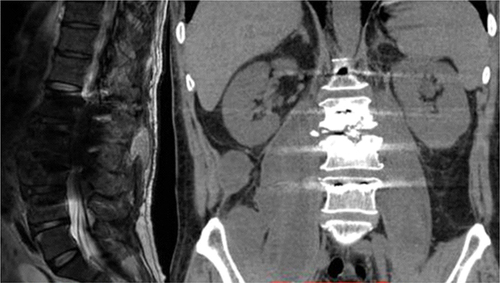
Figure 1 X-ray images showed uneven density and narrowing of the L2/3 intervertebral space (A and B). CT showed a cavity in the L2/3 segment of the vertebra, bone destruction involving most of the vertebra, and multiple irregular sequestrum (red arrow) within the lesion (C and D), Sagittal MRI showed vertebral body and intervertebral disc low T1 signal and high T2 signal. After enhancement, the abscess wall was significantly enhanced (E–H).
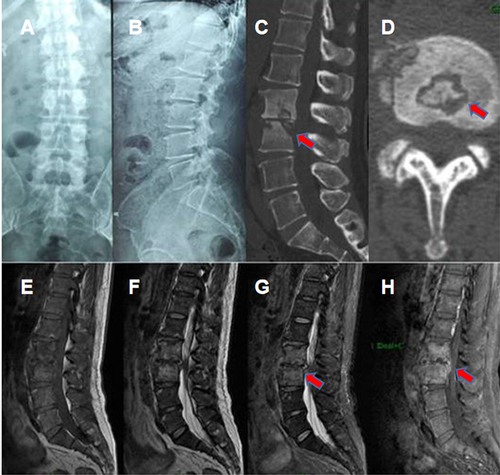
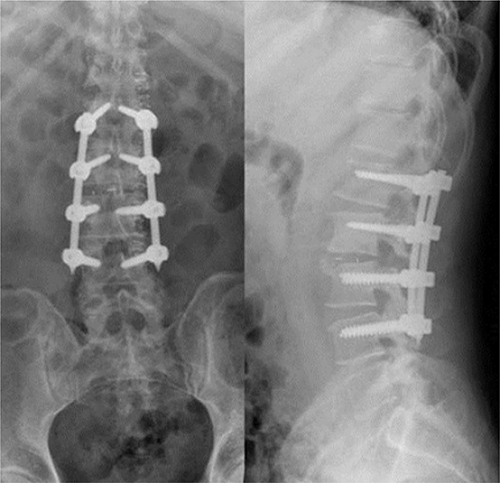
Figure 2 X-ray examination was performed on the third day after operation. The results showed that the internal fixation was firm and the position of the fusion cage was satisfactory.