Figures & data
Figure 1 Domain organization in MMPs.
Abbreviations: S, secretion signal; Pro, propeptide; Cat, catalytic; H, hinge region; Hpx, hemopexin; F, furin-recognition sequence; L, linker; G, glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor; TM, transmembrane; F2, fibronectin type II; CR, cysteine-rich; Cy, cytoplasmic; Zn, zinc.
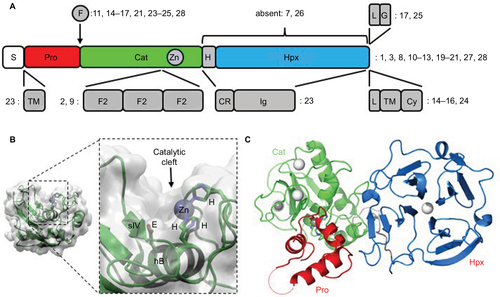
Figure 2 Kaplan–Meier curves of overall-survival probability across all glioma-tumor types in French data set separated based on MMP gene expression.
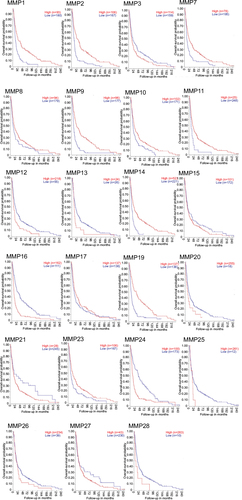
Figure 3 Gene-expression analysis of MMPs of 276 glioma samples of all histologies, with eight control samples.
Abbreviations: SEM, standard error of the mean; ANOVA, analysis of variance; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme.
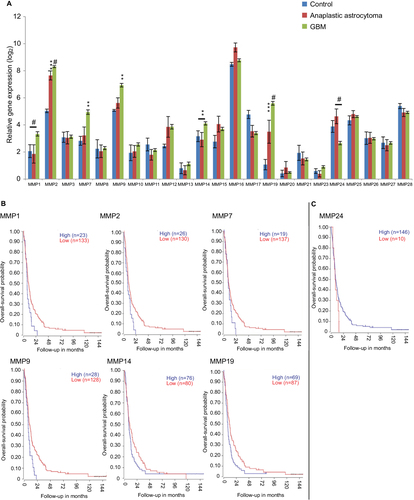
Figure 4 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR.
Abbreviations: PCR, polymerase chain reaction; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme.
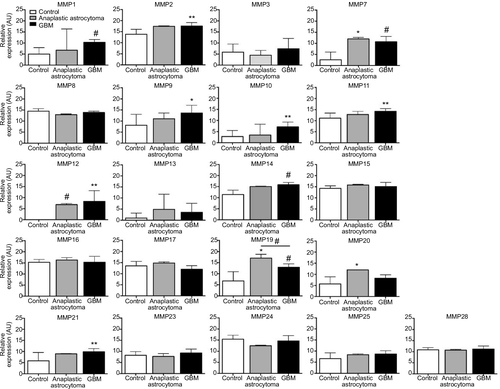
Table 1 Conserved and poorly conserved sites at the 3′-end of matrix metalloproteinases, for miRNA binding predicted by TargetScan
