Figures & data
Figure 1 Biosynthesis of E2 from cholesterol.
Abbreviation: E2, estradiol.
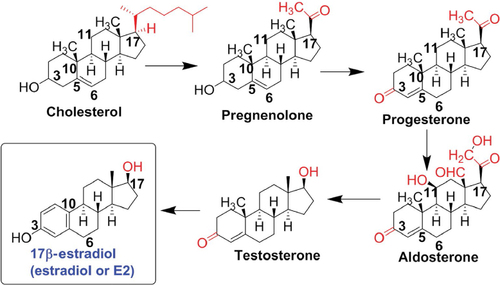
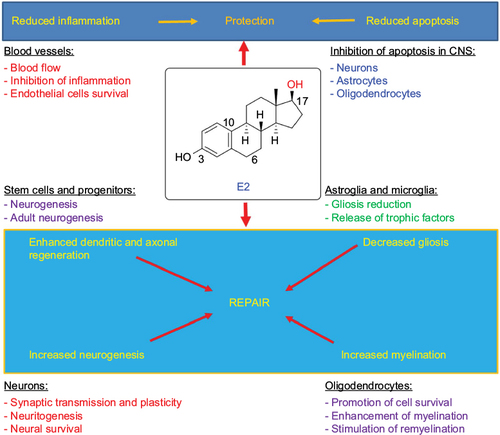
Figure 2 Various molecular mechanisms of E2 for its neuroprotective effects.
Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CNS, central nervous system; E2, estradiol; ER, estrogen receptor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
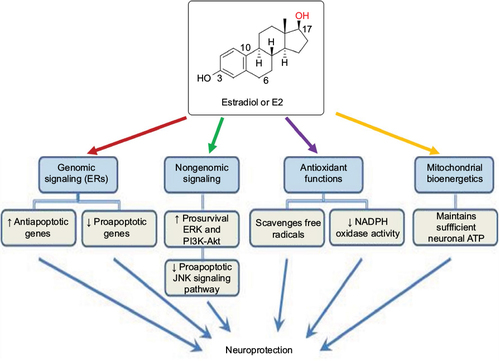
Table 1 The three main E2 receptors, their CNS locations, and their effects upon ligand binding
Figure 3 E2 has genomic signaling mechanisms for modulation of expression of various proteins for its neuroprotective effects in the CNS.
Abbreviations: CNS, central nervous system; E2, estradiol; ERs, estrogen receptors; MMP-9, matrix metalloprotease-9; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
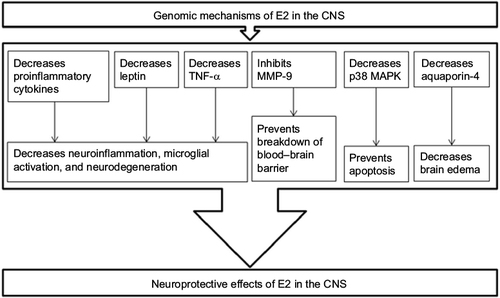
Table 2 Effects of MP, the current drug used for SCI treatment, and E2 in the spinal cord
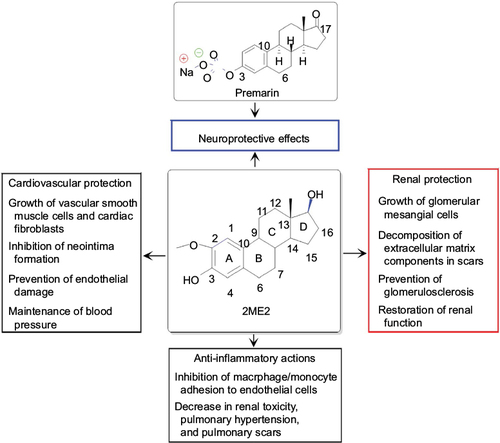
Figure 4 Chemical structures of the main component in Premarin and of 2ME2 and their therapeutic effects.
Abbreviation: 2ME2, 2-methoxyestradiol.