Figures & data
Figure 1 Schematic representation and photograph of the HIFU balloon.
Abbreviation: HIFU, high-intensity focused ultrasound.
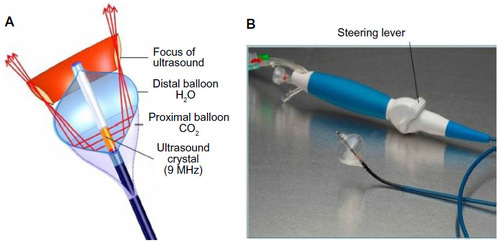
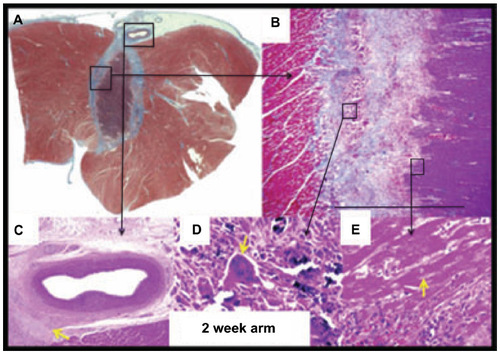
Figure 2 Lesion formation with HIFU.
Abbreviations: HIFU, high-intensity focused ultrasound; RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle.
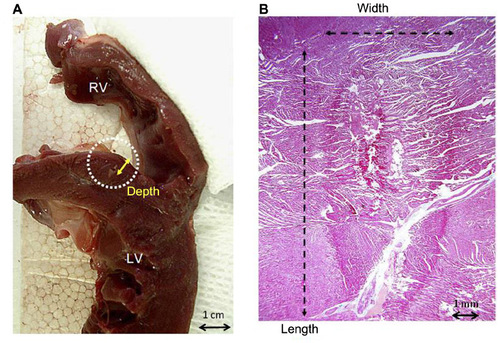
Figure 3 Location of structures prone to injury during balloon-based AF ablation.
Abbreviations: AF, atrial fibrillation; Ao, descending aorta; Eso, esophagus; HIFU, high-intensity focused ultrasound; LA, left atrium; RSPV, right superior pulmonary vein; RT PN, right phrenic nerve; SVC, superior vena cava.
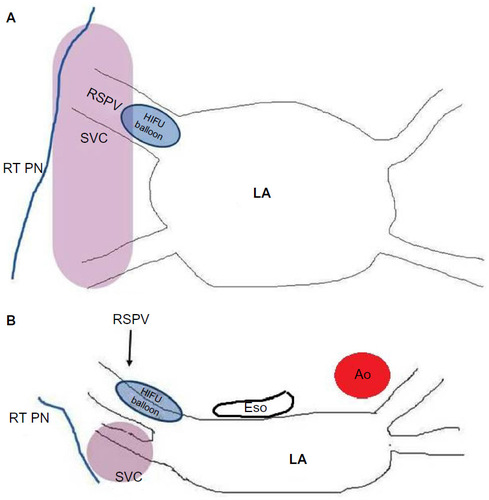
Figure 4 The Epicor epicardial HIFU system.
Abbreviations: HIFU, high-intensity focused ultrasound; AF, atrial fibrillation.
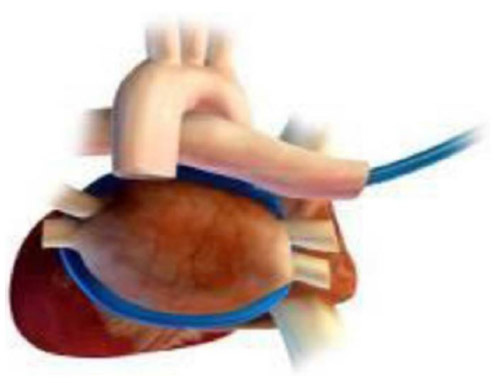
Figure 5 Epicardial ventricular ablation over a coronary artery.
Abbreviations: HIFU, high-intensity focused ultrasound; LAD, left anterior descending artery.