Figures & data
Figure 1 Retrosynthetic analysis of (A) 2-methyl-(4H)3-substituted quinazolin-4-one and (B) 2-phenyl-(4H)3-substituted quinazolin-4-one.
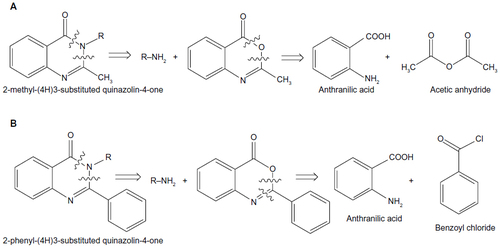
Figure 2 General synthetic route for (A) 2-methyl(4H)3-substituted quinazolin-4-one and (B) 2-phenyl(4H)3-substituted quinazolin-4-one.
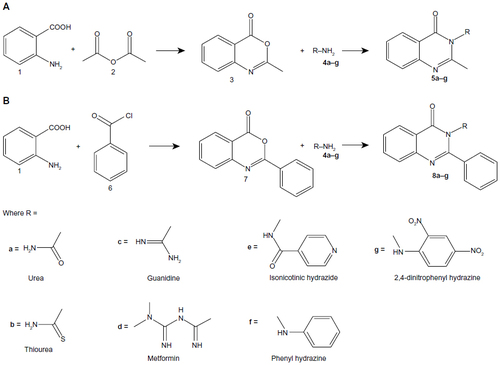
Table 1 The antitubercular activity (minimum inhibitory concentration [MIC] values and the binding affinities to InhA) for quinazolinone derivatives
Figure 3 The antibacterial activity of compounds 5a–g against Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus albus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
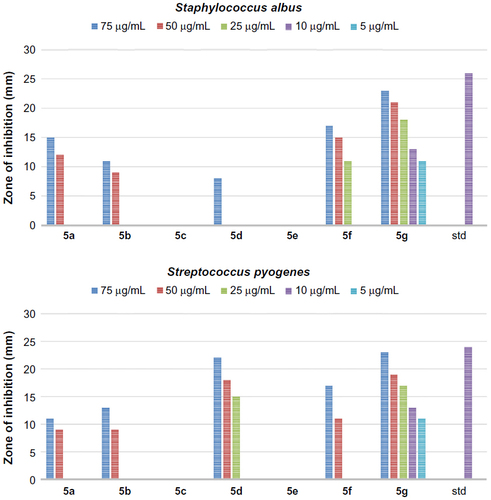
Figure 4 The antibacterial activity of compounds 5a–g against Gram-negative bacteria, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella.
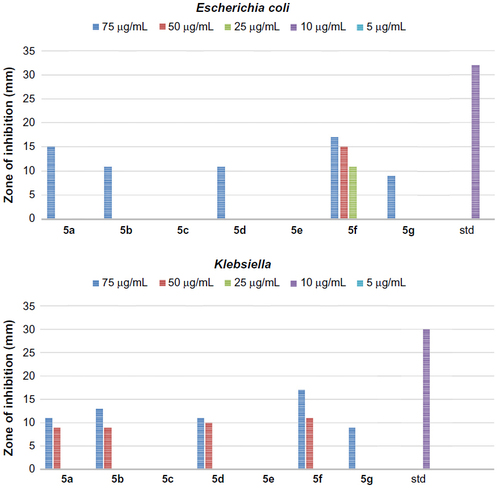
Figure 5 The antibacterial activity of compounds 8a–g against Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus albus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
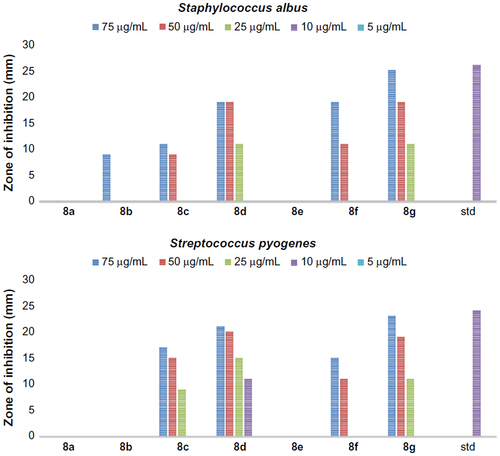
Figure 6 The antibacterial activity of compounds 8a–g against Gram-negative bacteria, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella.
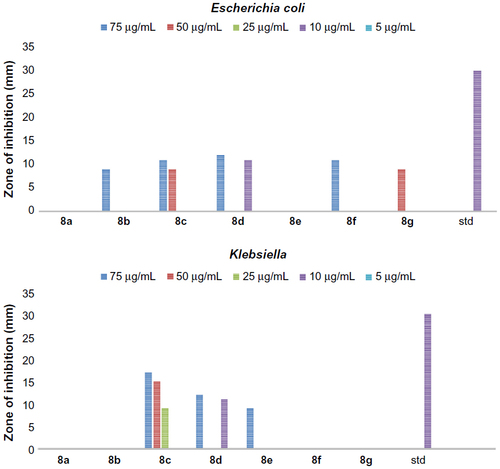
Figure 7 Ramachandran plot for the analysis of ψ and φ torsion angles for all residues on the macromolecule prepared for docking.
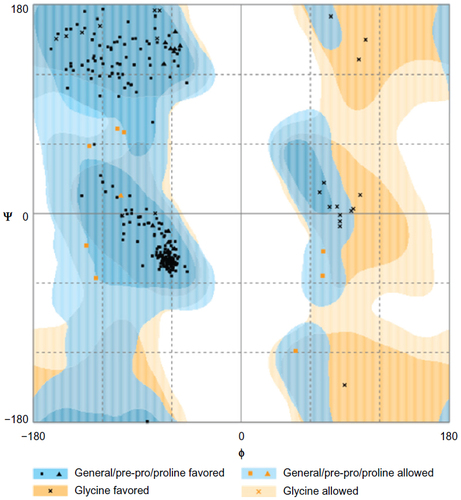
Figure 8 The alignment of the docked ligand on the X-ray crystal ligand in the active site of InhA.
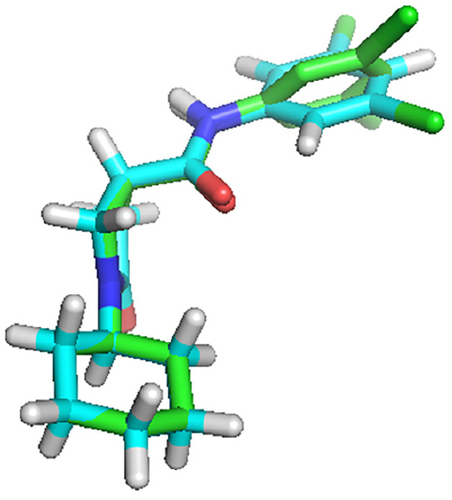
Table 2 Summary of the residues interacting with quinazolinone derivatives
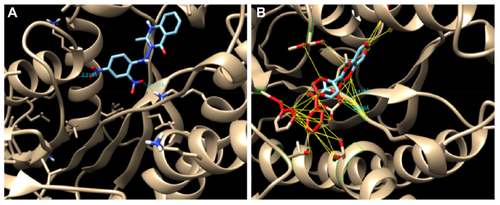
Figure 9 (A) Hydrogen bond (HB) interactions of compound 5g and (B) HB interactions and hydrophobic contact of compound 8c in the binding site of InhA.
Abbreviation: InhA, enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase.