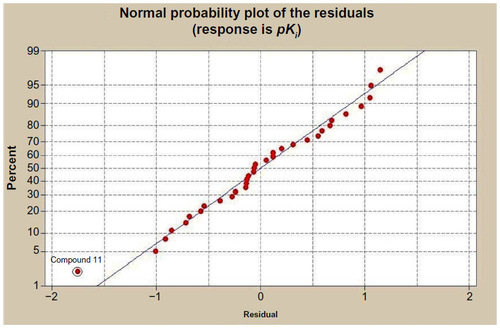
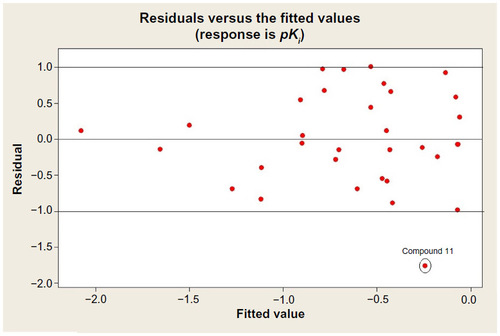
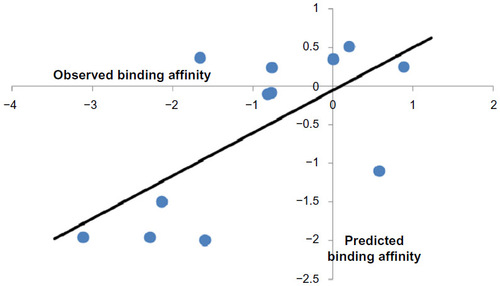
Figures & data
Table 1 Biological activity data
Table 2 Molecular descriptors used in this study
Table 3 Calculated structural invariants of a series of aminopyridazine derivatives of γ-aminobutyric acid
Table 4 T-values of the modeled parameters
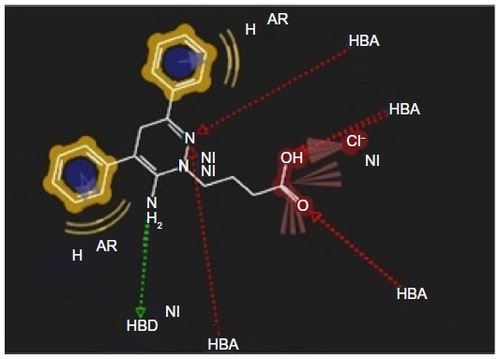
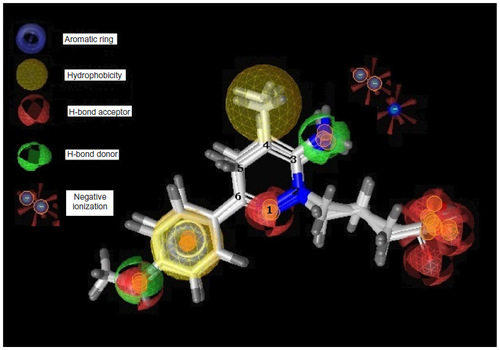
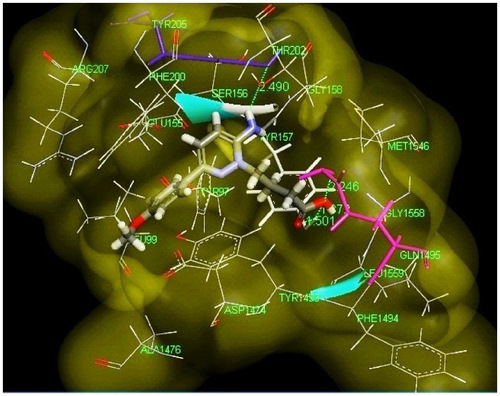
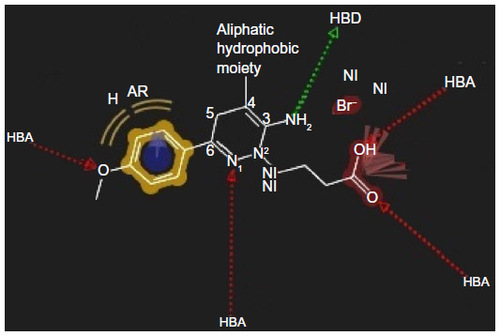
Figure 5 Pharmacophore model of low active compound number 11.