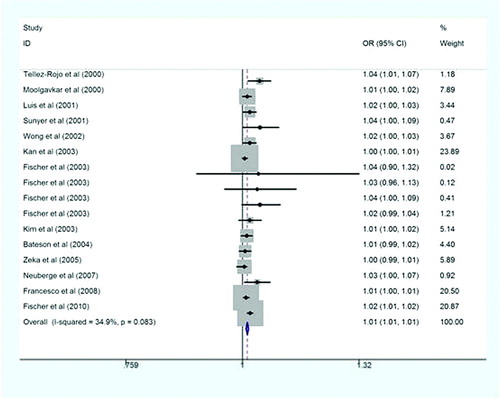
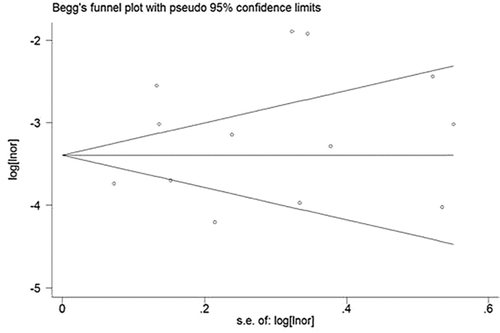
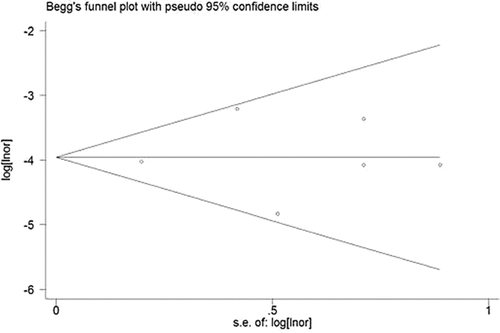
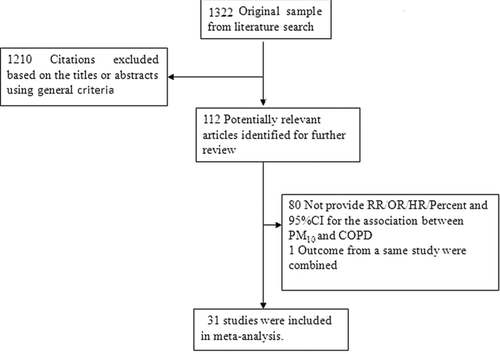
Figures & data
Table 1. Studies included in the meta-analysis investigating the short term effects between PM10 on COPD
Table 2. Studies included in the meta-analysis in different groups between PM10 and COPD hospitalizations and mortality
![Figure 2. Forest plot of COPD hospitalizations and PM10 in the meta-analysis Random-effect models were used to calculate the pooled effect size for OR (chi-squared χ2 = 117.82, [degree of freedom, df = 19], I2 = 83.9%, p < 0.001; and Z = 6.61, p < 0.001). The random pooled effect size (OR) for COPD hospitalizations due to PM10 was 1.03 (95%CI = 1.02–1.04).](/cms/asset/13954c8d-f715-47a8-a116-0e65fc7fcdcb/icop_a_744962_f0002_b.jpg)