Abstract
Purpose
Designing an Organizational Innovation Model with an Emphasis on the Approach of Lean Human Resources Management: The Case of Selected Municipalities of Mazandaran province.
Methodology
From a methodology point of view, this is a qualitative study, which is grounded theory and classified data were collected through interviewing the experts who agreed to participate in this research and were familiar with the topic including faculties in organizational innovation field and chief officers of selected municipalities of Mazandaran province.
Findings
The results showed that the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on lean human resources management approach has 156 indicators and 8 subcategories along with the lean innovation capabilities category, these subcategories are: lean human resources recruitment, supply and adjustment system, Lean human resource improvement system, lean human resource maintenance system, lean human resource application system, utilization of technology, organizational culture, organizational structure and policies and programs. In the following, all the dimensions, components and indicators of the three main dimensions are described; The enablers of lean innovation, the facilitators of lean innovation and the capabilities of lean innovation were summarized and purified.
Research limitations/implications
In the practical context, the results of the study can provide clear messages for the senior and middle managers of such organizations, so that based on those findings, they can formulate detailed operational plans with the aim of increasing internal innovations and also empowering their human resources.
1. Introduction
Today, organizations are facing many challenges and problems. The first serious issue and challenge that involves organizations is related to the lack of organizational dynamism due to the extensive global competition and the lack of organizational competitive advantages. The second issue that has led to the reduction of organizations’ power is the lack of transparency regarding the role of humans in creating a competitive environment and competitive intelligence in organizations. The third issue also refers to the increase in losses in carrying out organizational processes. Many organizations have taken measures to solve these problems. Some of these strategies and measures of innovative knowledge-creating organizations, multi-faceted organizations, agile organizations and multi-tasking employees. Multi-skill is a quality assurance and refinement system [Citation1]. One of the things that have been discussed in the past few decades is lean human resource management; lean human resource management means maximum use of human resources to achieve goals with minimal waste. One thing that has been discussed in the past few decades is lean human resource management; it means maximum use of human resources to achieve goals with minimal waste. Different views on the role of human resources and its management in the implementation of the lean approach indicate that the word ‘waste’ in the philosophy of the lean approach is limited to materials, time and cost, and the elimination of behavioral waste of human resources is one of the elements of the successful implementation of this approach, in such a way that the behavioral productivity of human resources is of equal importance to production productivity [Citation2]. Therefore, in today’s competitive environment, looking at human beings has exceeded the limit of a resource in such a way that the quality of human resources attracted and the way they are managed can lead to the creation of a competitive advantage in the field of business and competition [Citation3].
Today’s world is under continuous changes and transition and unsustainable conditions that have a crucial effect on organizations. Therefore, in order to survive, it is necessary for organizations to accommodate themselves to changes that threaten their vitality. In competitive markets, there is an urgent need to develop and improve flexibility and organizational responsibility. Many organizations encountered an increasing, continuous, and uncertain competition and due to their internal technological innovations, changing external environments and understanding of their clients’ needs could withstand these competitions [Citation4].
Increasing the importance of innovation and paying attention to this topic and consequently, fast changes in environments, have provided some situations in which for many organizations the speed of environmental changes is relatively higher than their responsibility and their accommodation ability. In other words, as soon as working conditions change and the organization decides to react and get matched with the changes, it faces another change. In such an atmosphere, organizations are quickly surrounded by opportunities and threats, since every innovation makes some changes that, in turn, can provide an opportunity for the organization to exploit this situation. In line with these facts, innovating and creating new thoughts and ideas and using them by managers and organizational employees, are very important and need to be considered important issues. In such a situation, only the organizations that improve their performance in important organizational competence such as innovation can continue their activities [Citation5].
Lean thinking is considered a new philosophy and attitude toward production and its orientation is located in Japan. Among its forerunners, Eiji Toyoda and Taichi Ohno can be mentioned here. This approach later developed in Europe and America and many organizations and companies accepted it. This method tries to minimize wasting and maximize exploiting facilities and human resources [Citation6]. Lean thinking is a social system and integrated technique whose main purpose is to banish wasting through decreasing or minimizing internal changeability and supplier and client’s changeability simultaneously [Citation7]. The fundamental concept of lean thinking has been rooted in eliminating waste and creating values in organizations. Lean thinking is an attitude that is based on increasing productivity, continuous value-creation, minimizing costs and wasting [Citation8].
The increasing speed of environmental changes and the intensity of competition between organizations have caused organizations to seek competitive advantages and better meet the needs of customers. Therefore, in order to overcome uncertain and complex conditions as well as stay dynamic in the field of competition, the only possible way for managers of organizations is to possess forceful and efficient human resources that are reckoned as valuable properties and assets of the organization [Citation9]. Undoubtedly, human resources of all ages have been the most important factor in development and have always been considered the impetus for development. Nowadays, when the human being has achieved incredible progress in science and technology, human resource’ importance decrease and it has increased due to paying more attention to human resource issues as a creating and employing technology [Citation10].
Reviewing the current literature in the field of lean services, we can realize that most of the studies conducted in this area are about production companies and the importance of lean has been ignored in relation to public and non-governmental organizations. The results show that some features of these organizations are similar to features of production centers. For example, their leadership and management systems are very similar; however, they differ in terms of focusing on clients and customers. Like other organizations, municipalities of Mazandaran province considering their needs for inter-organization innovations and utilizing their lean thinking capacities have to be consistent with other organizations and companies so that they can present better services to society. Applying the capacities maximally and the role of human resources are determinant factors in this journey. Regarding the above-mentioned explanation, the present study aims to respond to the following research question:
RQ: How does the model of organizational innovation emphasize a lean human resource management approach in selected municipalities of Mazandaran province?
The necessity of doing this research is today without using human resources, it is not possible to have the necessary effectiveness in the field of organizational innovations and the performance of institutions and organizations is directly influenced by human resources and their function. Because in the environment of today’s organizations, the development of internal innovations of the organization is inevitable and this happens when the employees have the necessary efficiency, effectiveness and quality (Swat and Salim, 2018). Due to the fact that there are limited sources regarding the research topic, the results of this study can be used in the scientific field for researchers who work in this field and the fields related to innovation, especially intra-organizational innovations, as well as the role of human resources in the organization, especially public organizations. Non-governmental organizations such as municipalities conduct research that is useful and illuminates new dimensions for them. Also, in the field of application, the results of the study can provide clear messages for senior and middle managers of such organizations, so that based on those findings, they can develop detailed operational plans with the aim of increasing internal innovations and also empowering their human resources. In other words, it can be said that the target society’s need for this research and the personal and professional interests of the researcher with a general view of the expected achievements are other factors that require the necessity and importance of this research.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1 Innovation in Organization
Innovation is a multiphase process through which persons realize the issue that should be solved, then present some ideas and solutions, and after that, put these ideas into action and introduce a model or paradigm to apply their ideas in the intended organization or its subsection [Citation11].
Innovation and creativity are the most important factors in success in today’s business world. According to the existing literature in this field, identifying the boundaries of creativity and innovation is still difficult and unclear [Citation12]. Creativity is related to cognitive and behavioral processes used while creating new ideas. On the other hand, innovation is related to the processes that are applied while attempting to execute these new ideas. Specifically speaking, innovation includes a combination of identifying a situation/issue, introducing, applying or revising new ideas related to organizational needs, refining the ideas and executing them. This integrated definition clearly states that in the working environment, creativity and innovation are two distinct but related concepts in such a way that creativity refers to creating new ideas and innovation refers to the attempts that are made to introduce, revise, refine and execute these ideas.
Innovational strategies show companies to what extent and how to employ innovation in order to improve their performance [Citation13]. They have defined innovation strategy in this way: predetermined, applicable and gradual design for the management of allocating resources to various kinds of innovations in order to achieve general strategic goals and propose a framework for guiding decision-making that is assigned to industries and companies. These are about the proper time for abandoning the history in the best condition or changing the company’s goals to concentrate on the future business.
2.2 Lean and Lean Thinking
In lean thinking, in order to improve production processes and establish an organizational environment to achieve long-term goals, some principles are taken into account. Identifying and applying these principles aids organizations in executing lean thinking. Nine identified principles of lean thinking are as follows:
Waste Removal: aim and philosophy of lean thinking are to reduce costs. This aim can be achieved by removing waste (whatever that does not add to the value of the product). Waste is something that customer is not willing to pay for it; consequently, it should be removed.
Continuous Improvement: when a production system produces continuously, its only goal is called culmination; if we consider waste removal as the most fundamental principle of lean thinking, continuous improvement can undoubtedly be placed at the next position.
Rate of Zero Defects: in order to achieve a higher level of productivity, it is necessary that parts and products be perfect and flawless from the early stages of production.
Production Update: the ultimate goal of production is to be on time and prompt exactly when the process needs a part.
Tensile Production System: opposite to the push production system, this is a tensile type of mass production system that was planned some months ago, the material is ordered and will be sent to the production line according to the plan. In the process of production, the part moves in a queue of actions and when one action ends, the part will be pushed to the next action. This technique needs sudden reactions and hardens making changes in production. To attain a lean production system, the tensile production system should change. The meaning of the push system is not that nobody should produce any product or provide any services, except for the client who should have ordered it before. In many prevalent systems like these, the client gets the products and then the producer fills the blank space of the taken product. Applying the concept of tensile is slightly complicated.
A Multi-Functional Team: the most prominent characteristic of organizing a lean thinking job is to increase the use of multifunctional teams.
Decentralization of responsibilities: decentralization of responsibilities and assigning them to some multifunctional working teams is another important characteristic of organizing lean thinking.
Aggregating the tasks and duties: aggregating different tasks in the form of the teams means that all the tasks that were accomplished by indirect sections before, would be assigned to the teams’ duties; consequently, the content of the team’s tasks would increase.
Vertical Information System: information is very significant in reinforcing multifunctional teams in order to achieve organizational goals. In fact, what makes improving companies’ performance difficult, is selecting the best and the most effective strategy regarding the organization’s characteristics.
Lean thinking is a complete system that utilizes continuous improvement philosophy and team working culture and endeavors to detect, analyze and banish existing wastes. This system has been designed in such a way that it can continuously measure the improvement of production flow and reduce waste. Actually, lean production is a systematic attitude that aims to banish dregs and wastes and eliminate every unnecessary process in every phase from supplying material to the production and selling stages [Citation14].
2.3 Lean Human Resource Management
Currently, more than two decades have passed since the emergence of the lean revolution in the world’s manufacturing industries, so the desire to use production improvement methods, including the lean approach, which is rooted in the thinking of Taylor (1911), Ohno (1978) and Deming (1986) has it. It has increased significantly and its implementation is reflected in the actions of managers with the aim of creating value for the stakeholders (Nguyen, 2018). Being lean can be considered as creating the most added value with the least capital [Citation15] that in all the steps required to produce a product or service, from the initial idea to the production, from the raw materials to the delivery of the final product to the customer, the concept of value from the customer's point of view is taken into account and quickly seeks to identify and eliminate all non-value activities. It is the waste in the system [Citation16]. The lean approach in terms of nature and construction is a complex sequence of activities, plans and programs that reaches its peak for optimal use in the field of physical implementation and completion of the structure [Citation17]. The basic concept of the lean approach lies in the eradication of waste and value creation in the organization, which is used in order to increase productivity and continuous value creation in the organization, in such a way that it can be done with the least resources (materials, equipment, manpower, time and cost) did the most work [Citation3].
The National Association of Standards and Technology in the US Department of Commerce has defined lean production as follows. A systematic solution to identify and eliminate waste (activities that do not add value) through continuous improvement and streamlining production just when the customer needs it [Citation18].
Human resources are considered the most valuable assets of any organization. In other words, the effectiveness and success of any organization depend on the people who are the components of that organization and do their job [Citation19]. Amazing and profound progress in various sciences and technologies and its effects on various fields and administrative and service activities of institutions and organizations have raised the need for training, and improvement of human resources working in an organization and has made it necessary [Citation20].
A successful organization is a collection of persons with common thoughts, ideas and goals who, due to their passion for growing progress, share their experiences and knowledge with their organization through teamwork in a flexible system of their organization. Staff training and empowerment is one of the goals of organizations and is always based on the belief that productivity depends on educated and capable employees. Today’s organizations are under a lot of pressure due to factors such as increasing global competition, sudden changes, the need for quality and after-sales services, limited resources and so on.
The importance of human resources role in organizations is undeniable. The human force is the most efficient tool to achieve preplanned goals [Citation21]. In all organizations, human force possesses a particular position and is considered the main asset of the organizations [Citation22]. In some major organizations, this position is particularly more important since it is a process through which the force of access to the future vitality of society will grow and develop in addition to being a factor of growth and development and increasing knowledge and technology needed by society [Citation23].
Usually, until the last four decades, management and scientific principles used in production organizations were used in service organizations, and the belief that achieving economic scale leads to a reduction of unit costs, as the main. It was considered the most important feature in management decisions [Citation24]. From the late 1970s onwards, there is evidence of the transfer and application of lean manufacturing concepts to the service sector. Because this approach focuses on cost management and employee activities, the increase in productivity has brought with it the performance of the organization [Citation25].
Derived from the definitions and principles of the lean approach, lean human resource management is a set of strategic actions that by strengthening the role of the human resources unit, improves the functions of human resources and minimizes the waste of employees’ abilities and talents, improves financial results and increases. It leads to customer satisfaction [Citation26].
3. Review of the Literature
Taheri and Rostamlou (2018) [Citation27] examined the effects of the functions of human resource management on innovation. They conducted this study using 107 samples selected from knowledge enterprises in the Science and Technology Park at the University of Tehran. Results showed that functions of human resource management have a significant and direct effect on employees’ creativity and innovation in production. Mirghasemi and Noor (2015), [Citation6] through a case study, studied effective factors in evaluating service provider organizations regarding using lean production concepts in Shahid Ansari Hospital in Roodsar. In this study, a model of lean factors, including four main criteria and 23 peripheral criteria, was extracted and then was screened with mentioned hospital using a questionnaire. Zamani and Heidari (2013) in a study titled ‘interaction between lean production and agile manufacturing’ stated the fundamental principles and approaches of lean production as well as its relationship with agile manufacturing. They categorized fundamental principles of lean production into three groups, namely, human resources and organizational components, providers and production system. In discussing the separation of lean production and agile manufacturing, they emphasized providing a section. Furthermore, they concluded that lean thinking intends to provide market productions with high quality and low cost while agile manufacturing intends to provide particular products with less delivery time as soon as possible. Adro, F and C, Leitao (2020) [Citation28] probed leadership and organizational innovation. It was a systematic review of related literature on organizational innovation. Among the collected articles, 144 articles were selected and reviewed systematically. Results showed that there are some concerns in terms of management bodies in different sections and the lack of proficient leaders [Citation29] scrutinized capabilities of innovation derived from social networks. Moreover, they examined how clients’ conversations turned into organizational innovations. Findings revealed that social networks have many capabilities for innovation in organizations and all the suggestions, critics, comments and conversations in social networks could turn into organizational innovation in various sections.
Andersson et al., (2020) [Citation30] investigated the organizational climate for mental security related to the innovation capabilities of small and medium companies and their innovation performance. The results exhibited that organizational climate covers the mental security of organization employees and can positively be connected to innovation performance and increase innovational capabilities of these small and medium companies.
4. Methodology
Considering purpose and nature and from the methodological point of view, this study is a qualitative one that is conducted by interviewing experts who were familiar with the topic. They included faculties in the field of organizational innovation and human resources, as well as chief offices in selected municipalities of Mazandaran province. In this stage, sampling done in a theoretical way was selected from events, not necessarily persons. Even if persons are considered, the main and key purpose is inquiring about the events. However, there is no specific role for sample size in qualitative research design, for homogeneous groups 6–8 units and for heterogeneous groups, 12–20 units are selected. The interviews were continued until theoretical saturation was achieved. In this study, we reached saturation status after interviewing 12 experts (faculties of innovation in organizations and the human resource field and chief officers of selected municipalities in Mazandaran province). Sampling was accomplished purposefully with a framework based on qualitative logic. The sampling was purposeful and snowballed. Usually in qualitative research, in order to collect the maximum amount of data, purposeful sampling is applied. Therefore, the researcher chose those participants who were the so-called ‘full of information’. In other words, based on the qualitative research maxims, some samples were selected that present a detailed and vivid picture of an understudy phenomenon. Selecting participants based on the purposeful sampling method was performed in some universities which were willing to take part in interviews. Regarding the vast prevalence of COVID-19 and all limitations and healthcare principles, the researchers utilized some other kinds of interviews except for face-to-face, for example, recording audio files, email and WhatsApp. The basis of the qualitative section of the present study was grounded theory and three types of coding (i.e. open, axial and selective coding) were hired. Data analysis was done with MAXQDA computer software. Grounded theory (that is known as a theory emerging from data, context theory and fundamental theory) is a general, inductive and interpretive research design that was established by Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss in 1967 [Citation31].
5. Results
5.1 Identifying Research Indices (Open Coding)
The analysis process begins as the researcher reviews and reads the typed interviews line by line in connection with the design of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on the lean human resource management approach (case study: selected municipalities of Mazandaran province) and it codes and classifies similar data that have the same semantic load under common codes and then assigns appropriate concepts to each of the classes. During this stage, which is called open coding, various and numerous categories were extracted in relation to the design of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on the lean human resource management approach. These concepts were adapted from the writings and in some cases the same writings, in total, after removing approximately thirty percent of them, 156 primary codes (indexes) were created from a total of 12 interviews. Then, due to the plurality of similar codes, based on conceptual and semantic affinity, they were placed in their own group and reduced to 8 sub-categories (dimensions) along with the category of lean innovation capabilities.
In the following section, we have advanced designing and provided an organizational innovation model with an emphasis on the human resource management approach in selected municipalities of Mazandaran province through the tables of coding conducted interviews.
After talking with the esteemed supervisor, consultant and other professors participating in the research, all dimensions, components and indicators were summarized as follows.
5.2 Axial Coding
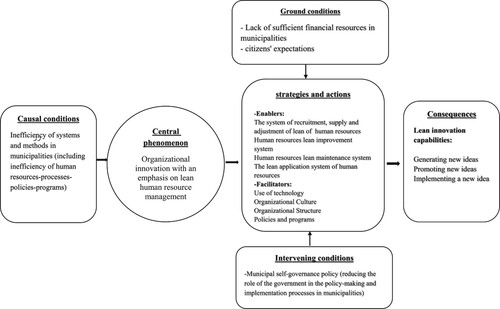
The second stage of data analysis in grounded theory is axial coding. The purpose of this stage is to establish a relation among created categories in the open coding stage. The relation between other categories and the core category can be found under five themes: causal conditions, central phenomenon, strategies and actions, intervening conditions, ground conditions and consequences [Citation32].
At this stage, when the categories are formed, the researcher chooses a category whose traces are visible in all the different parts of the data. This category, which is called the core category, was extracted under the core coding of the data, and one can find the origin and root of all the issues related to the design of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on the pure human resource management approach. At this stage, the researcher tried to find out how the relationship between each of the other categories is with the central category. At this stage, the position of other categories is determined around the central category. That is, the researcher has tried to identify the causal, intervening, contextual conditions, strategies and consequences among other categories.
Therefore, according to the opinions of respected professors and experts, based on the secondary coding results of the research, the subcategories in relation to the main categories (paradigm model categories) in the design of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on lean human resource management (case study: selected municipalities of the province Mazandaran) were selected as described in the tables. Tables .
Table 1. Dimensions, components and indicators.
Table 2. The main dimensions of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on lean human resource management.
Table 3. Main categories and subcategories of research.
5.3 Selective Coding
Mixing the data is very important in grounded theory. In the process of research, after collecting, analyzing and interpreting the data, it is time for presenting a model, concluding, summating and generalizing the results of the research. According to the opinion of the professors and experts, 156 indicators have been used in the design of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on the lean human resource management approach (case study: selected municipalities of Mazandaran province) from all the indicators obtained from the qualitative analysis of the content of the interviews. In the first step, by examining the current situation, the obtained data are classified into 8 subcategories along with the capabilities of lean innovation. Axial coding is the second step of analysis in foundational data theorizing. The purpose of this stage is to establish the relationship between the classes produced in the open coding stage. The relationship of other classes with the central class can be realized in five topics, which are causal conditions, strategies and actions, intervening conditions, contextual conditions and consequences (Strauss and Corbin, 2015). In the next step, we are looking to design an organizational innovation model with an emphasis on a lean human resource management approach (case study: selected municipalities of Mazandaran province), perform selective coding based on the theoretical model and finally present the model. In fact, in the final stage, through reviewing, refining and completing the categories and concepts extracted from the data, the design of the organizational innovation model has been created with an emphasis on the lean human resource management approach (case study: selected municipalities of Mazandaran province). The researcher presents the final model according to his understanding of the text of the phenomenon under study.
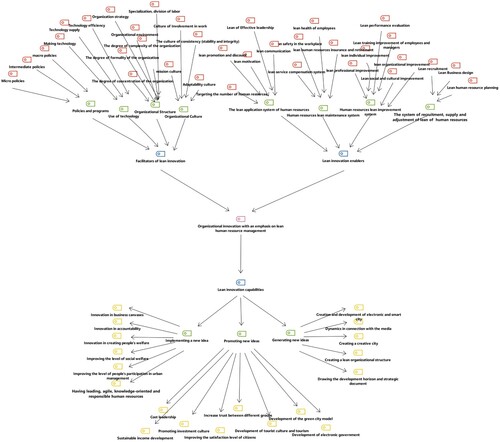
The figure below shows the paradigm model of organizational innovation model with an emphasis on lean human resources: The case of selected municipalities of Mazandaran province (). and The output of maxqda software is shown in .
6. Discussion and Conclusion
6.1. What are the Main Elements of the Organizational Innovation Model with an Emphasis on Lean Human Resource Management Approach (Dimensions, Components and Indicators)?
In the current research, from all the indicators obtained from the qualitative analysis of the content of the interviews, 156 indicators were created in the design of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on the lean human resource management approach (case study: selected municipalities of Mazandaran province) from a total of 12 interviews. Then, due to the abundance of similar codes, these indicators were placed in their own group based on conceptual and semantic affinity and were reduced to 8 subcategories (dimensions) along with the category of lean innovation capabilities: absorption system, lean supply and adjustment of human resources, lean human resource improvement system, lean human resource maintenance system, lean human resource utilization system, utilization of technology, organizational culture, organizational structure and policies and programs.
In the following, after talking with the respected supervisor, consultant and other professors participating in the research, all the dimensions, components and indicators are divided into three main dimensions as follows. The enablers of lean innovation, the facilitators of lean innovation and the capabilities of lean innovation were summarized and purified.
The components of the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on lean human resource management approach (case study: selected municipalities of Mazandaran province) include: lean human resource planning, lean job design and lean employee selection for the category of recruitment, supply and Lean adjustment of human resources; lean performance evaluation, lean educational improvement of employees and managers, lean organizational improvement, lean individual improvement, lean professional improvement and lean socio-cultural improvement for the category of lean human resource improvement system; Lean service compensation system, lean employee health, lean work environment safety and lean human resource insurance and retirement for the lean human resource maintenance system category; effective lean leadership, lean communication, lean motivation, lean promotion and demotion and targeting the number of human resources for the category of lean human resource utilization system; technology construction, technology supply and technology efficiency for the category of technology utilization; the culture of participation in work, the culture of compatibility (stability and integrity), the culture of adaptability and the culture of mission (mission) for the category of organizational culture; organization strategy, organization environment, degree of formality of the organization, degree of organization concentration, degree of complexity of the organization and specialization and division of work for the category of organizational structure; micro-policies, medium policies and macro-policies for the category of policies and programs, and finally, generating new ideas, promoting new ideas and implementing new ideas for the category of pure innovation capabilities.
Many organizations encounter many problems in their environment in terms of competition and these problems are due to the high speed of changes in the environment, especially technological changes. In this regard, managers and employees should utilize their creativity and innovation power to adapt and accommodate rapid changes, production lines, management practices and production processes [Citation33–35]. In fact, innovation is an essential and vital factor for organizations in order to establish sustainable value and virtue of competition [Citation36–38], and more innovation can cause more success for organizations to respond to changes in the environment as well as establish and develop new capabilities that allow them to reach a better performance [Citation39]. Lean thinking is an attitude to increase productivity and continuous value creation and minimize costs and waste. Lean production is actually philosophy, and an attitude that seeks to eliminate and remove any additional process that does not create added value from the preparation stage of raw materials to production and finally selling.
In addition, lean human resource management can also be very important for organizational innovation. Employee innovation in the workplace is a complex behavior that comprises a three-stage process. In the first stage, the innovative person understands the problem and offers solutions and ideas that may be either new or adapted. Then, this person tries to improve his/her idea and solution and find logical rules to defend this idea.
In the final stage, the innovative person presents an empirical model or paradigm for the implementation of ideas and solutions so that these ideas can be used in a group or organization. Lean production is a kind of production system that uses the benefits of both mass production and production custom (manual) and is designed with the aim of reducing waste and eliminating activities without added value. The main philosophy of this production system is to be perfect and flawless.
6.2. What is the Ratio and Relationship of These Elements with Each Other in the Organizational Innovation Model with an Emphasis on Lean Human Resources?
In order to investigate the relationship between the dimensions and the main components of the final model, in addition to the path coefficients that we discuss below, correlation analysis was also used. The results of the research showed that according to the coefficient of the path of lean innovation capabilities on the implementation of new ideas, the implementation of new ideas has a significant effect on explaining the capabilities of lean innovation.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation capabilities on new idea promotion, the new idea promotion has a significant effect on explaining lean innovation capabilities.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation capabilities on new idea generation, the new idea generation has a significant effect on explaining lean innovation capabilities.
According to the coefficient of the path of enablers of lean innovation on the lean improvement system of human resources, the lean improvement system of human resources has a significant effect on explaining the enablers of lean innovation.
According to the coefficient of the path of enablers of lean innovation on the system of absorption, supply and lean adjustment of human resources, the system of absorption, supply and adjustment of human resources has a significant effect on explaining the enablers of lean innovation.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation enablers on lean human resource maintenance system, the lean human resource maintenance system has a significant effect on explaining lean innovation enablers.
According to the path coefficient of the enablers of lean innovation on the system of lean use of human resources, the system of lean use of human resources has a significant effect on explaining the enablers of lean innovation.
According to the coefficient of the path of the facilitators of lean innovation on the use of technology, the use of technology has a significant effect on explaining the facilitators of lean innovation.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation facilitators on organizational structure, the organizational structure has a significant effect on explaining lean innovation facilitators.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation facilitators on policies and programs, the policies and programs have a significant effect on explaining lean innovation facilitators.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation facilitators on organizational culture, the organizational culture has a significant effect on explaining lean innovation facilitators.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation facilitators on lean innovation enablers, lean innovation facilitators have a significant and positive effect on lean innovation enablers.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation facilitators on lean innovation capabilities, lean innovation facilitators have a significant and positive effect on lean innovation capabilities.
According to the path coefficient of lean innovation enablers on lean innovation capabilities, lean innovation enablers have a significant and positive effect on lean innovation capabilities.
Innovation is one of the vital factors in the success of organizations that are often defined as the introduction and conscious use of ideas, processes, products or procedures that are new to different sections of the organization and its acceptance significantly leads to value creation for the organization (Peng et al., 2014). Prajogo and Daniel (2015) believe that in the field of production, a successful organization is to use innovative strategies regularly according to the market situation to overcome the uncertain competition caused by turmoil in the international markets. Numerous studies have been conducted to identify the effective factors in overcoming environmental uncertainty and many components have been proposed to organizations to overcome this competition, but using innovation to overcome these conditions has largely been emphasized by researchers compared with other cases (Rahimnia et al., 2018).
7. Practical Suggestions
According to the results of this study, the following suggestions can be made:
Considering that the results showed that the organizational innovation model with an emphasis on a lean human resource management approach includes the categories of lean human resource recruitment, supply and adjustment system, lean human resource improvement system, lean human resource maintenance system and lean human resource utilization system. Taking advantage of technology, organizational culture, organizational structure and policies and programs along with the category of lean innovation capabilities, it is suggested that the system in the field of recruitment, supply and adjustment of human resources should adopt mechanisms that lead to the effectiveness and efficiency of activities such as forecasting demand and supply of human resources, gap analysis, accurate determination of various components of a job position, employment tests (interviews and questionnaires), discovering lean human resources and so on.
It is suggested that the system in the field of the lean human resource improvement system should adopt strategies that lead to the high efficiency of employee commitment, independent learning, problem-solving skills, creativity and innovation, sharing of findings, compliance with professional ethics and so on.
It is suggested that the system in the field of lean maintenance of human resources should adopt mechanisms that lead to more effectiveness and efficiency of activities such as establishing internal and external justice in the service compensation system, the health and exercise status of employees, the rate of occupational diseases and unemployment insurance. and pension fund services and such.
It is suggested that the system in the field of lean use of human resources should adopt strategies that lead to the high efficiency of group empowerment, sincere empathy, fulfillment of customer expectations, talent assessment and so on.
It is suggested that the system in the field of using technology should pay special attention to suitable information infrastructures, support of managers and ease of use of services, because in most organizations these indicators are not given much attention or execution time is missed.
It is suggested that the system in the field of organizational culture promotes the culture of participation and the culture of stability and sustainability more and tries to institutionalize the fundamental values of the above concepts in the organization.
It is suggested that the system in the field of organizational structure should pay special attention to the environmental factors affecting it because the condition of survival and durability for organizations is to adapt to the changes in the surrounding environment and despite many claims, the inability of the system to adapt to the changes of political factors, social, cultural and economic is evident.
It is suggested to adopt policies and programs that have high implementation capability and flexibility, and on the other hand, timely and appropriate strategies are used in conflict management and situations of doubt and threat.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Additional information
Notes on contributors
Ebrahim Ghasemzadeh
E. Ghasemzadeh was born on July 24, 1983 in Babolsar, Mazandaran, Iran. he received his M.SC in the field of human resource management. Currently' He is a PH.D. student in public administration with a specialization in human resource management, a university lecturer and a municipal financial manager.
Mohammadreza Bagherzadeh
Mohammadreza Bagherzadeh, Assistant Professor of Public Administration, Department of Management, Ghaemshahr Branch Islamic Azad University, Ghaemshahr, Iran. [email protected]
Seyedahmad Jafari kelarijani
Seyedahmad Jafari kelarijani, Assistant Professor of Public Administration, Department of Management, Ghaemshahr Branch Islamic Azad University, Ghaemshahr, Iran.
Ezzatollah Baloui jamkhaneh
E. Baloui jamkhaneh received his M.Sc. at Ferdowsi University of Mashhad and PH.D at Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch. He is an Associate Professor at Islamic Azad University of Iran. His research interests include applied statistics, fuzzy reliability, fuzzy quality control, and intuitionistic fuzzy sets theory.
References
- Anahid M. Human resources and innovation operations in the organization. Humanit Res. 2012;30(5):45–60.
- Nguyen M. A new decision making model based on the made in Vietnam lean management philosophy. Econ Sociol. 2018;11(1):44–60.
- Mayer A, Weigelt M, Kuhl A, et al. Lean 4.0 - A conceptual conjunction of lean management and Industry 4.0, Procedia CTRP, 51st CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems. 2018; 72: 622–628.
- Aizhan T, Franco M, Pagliari C. Use of social media for e-government in the public health sector: a systematic review of published studies. Gov Inf Q. 2017;34:270–282.
- Rajabi M, Hassani M, Mohajeran B. An investigation of the role of human resource development activities on employee’s innovation by examining the mediating role of knowledge management and organizational learning among the staff of Imam Khomeini relief foundation, West Azerbaijan Province. J Innov Creativity Humanit. 2016;6(3):151–178.
- Mir Qasemi, S., & Noor, M. Determining and examining the effective factors in evaluating service organizations in applying the concepts of lean production: a case study on Shahid Ansari Hospital in Rudsar. Third international conference on challenges and solutions management, 2015
- Shah R, Ward PT. Defining and developing measures of lean production. J Oper Manage. 2007;25(4):25–34.
- Asgari H. Elements and tools of lean production. Qual Control Month. 2013;10:48.
- Dehghani M, Hamedi S, Javaran HR. The effect of social support and the level of working life quality in psychological empowerment of the staff of the ministry of cooperatives, labor and social Welfare of Kerman. J Cooperatives Agric. 2017;6(21):30–66.
- Shahrakipour H. The effect of agility on empowerment of executive staff of Zahedan. Educ Manag Innov. 2017;12(3):117–140.
- Faleh M, Nayebzadeh S, Davoodi A. The effect of organizational learning on competitiveness with respect to the role of innovation with an structural equation approach: a case study on telecommunications of Yazd region. New Res Approaches Manag Account. 2018;6:163–175.
- Escriba-Carda N, Canet-Giner MT, Balbastre-Benavet F. The key role of human resources practices in the promotion of creativity and innovation: a Spanish case study. In: Hervas-Oliver JL, Peris-Ortiz M, editors. Management innovation. Springer proceedings in business and economics. Cham: Springer; 2014. Global Innovation Index, 2018. Data from https://www.globalinnovationindex.org/analysis-indicator.
- Lendel V, Varmus M. Creation and implementation of the innovation strategy in the enterprise. Econ Manag. 2011;16(1):819–825.
- Ahmadi A, Maleki MH, Jafarnejad A. An evaluation of lean production using a mix of ANP and DEMATEL techniques in fuzzy conditions. Sci-Res Q Manag Stud. 2011;8(20):1–25.
- Agarwal A, Shankar R, Tiwari MK. Modeling the metrics of lean, agile and leagile supply chain: an ANP-based approach. Eur J Oper Res. 2006;77:200–222.
- Kadarovaa J., Demeckoa M. 3rd global conference on business, economics, management and tourism, Procedia Econ Finance, (2016); 39: 11–16.
- Bhasin S, Burcher P. Lean viewed as a philosophy. J Manuf Technol Manag. 2006;7(0):72–22.
- Aziz R, Hafez S. Applying lean thinking in construction and performance improvement. Alexandria Eng J. 2013;52(4):679–695.
- Rodriguez C, Vilana JR. Analysis of global manufacturing virtual networks in the aeronautical industry. Int J Prod Econ. 2010;126:314–323.
- Arion Bayar S, Cang S, Yu H, et al. Predicting the relationships between virtual enterprises and agility in supply chains. Expert Syst Appl. 2017;84:58–73.
- Khordegir S, Askari A, Ranjbar M. A study of human resource improvement indicators and its effect on staff performance. Q J New Approach Educ Manag. 2017;8(2):245–262.
- Drucker P. Challenges of management in the 21st century, translated by Mahmoud Tolouei. Tehran: Rasa Cultural Services; 1999.
- Bigdeli M, Davoodi R, Kamali N, et al. Identifying the dimensions and components of human resource improvement in education to provide a conceptual model. Q J Hum Resour Manag Res Imam Hossein Univ. 2018;10(2):75–101.
- Effah -Kesse D. Implementation of lean in the public sector: investigating the benefits and drawbacks, logistics at molde university college – specialized university in logistics, Master’s degree thesis, Molde University College, Norway. 2017.
- Eirian L. Better for less’ lean sigma for the public sector. London: TEAL Consulting Ltd; 2013.
- Jekiel CM. Lean human resources; redesigning HR processes for a culture of continuous improvement. 1st ed. Published by Productivity Press; 2011.
- Taheri G, Rostam Lou R. Investigating the effect of human resource management functions on productivity and innovation in the product and process: a case study on knowledge-based companies located in the science and technology park of the University of Tehran. Innov Manag. 2018;7(2):47–68.
- Adro F, Leitao C. Leadership and organizational innovation in the third sector: a systematic literature review. Int J Innov Stud. 2020;4:51–67.
- Patroni J, Von Briel F, Recker J. Unpacking the social media – driven innovation capability: how consumer conversations turn into organizational innovations. Inf Manag. 2020: 103267, doi:10.1016/j.im.2020.103267.
- Andersson M, Moen O, Brett PO. The organizational climate for psychological safety: associations with SMEs ‘innovation capabilities and innovation performance. J Eng Tech Manage. 2020;55:101554, doi:10.1016/j.jengtecman.2020.101554.
- Glaser B, Strauss A. The discovery of grounded theory. Chicago: Aldine Publishing Company; 1967.
- Strauss, A. & Corbin, J. (1998). Basics of qualitative research: techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory, 2nd ed., Sage. Thousand Oaks, CA.
- Zemaitis E. Knowledge management in open innovation paradigm context, high-tech sector perspective. Proc Soc Behav Sci. 2014;110(164e):173.
- Damanpour F, Walker RM, Avellaneda CN. Combinative effects of innovation types & organizational performance: a longitudinal study of service organizations. J Manage Stud. 2009;46(4):650–675.
- Sadeghi Mal Amiri, M. (2015). Systematic theory of creativity in organization. J Innova Creativity Humanit, 4, 163-207.
- Mina A, Bascavusoglu-Moreau E, Hughes A. Open service innovation and the firm’s search for external knowledge. Res Policy. 2014;43(5):853–866.
- Mura M, Lettieri E, Radaelli G, et al. Promoting professionals’ innovative behavior through knowledge sharing: the moderating role of social capital. J Knowl Manag. 2013;17(4):527–544.
- Wu C, Wang A. Geographical FDI knowledge spillover and innovation of indigenous firms in China. Int Bus Rev. 2016;25(4):895–906.
- Amiri M. A study of the relationship between knowledge management and strategic entrepreneurship based on mediated organizational innovation: a case study on Fars education organization. J Innov Creativity Humanit. 2018;8(2):147–184.