 ?Mathematical formulae have been encoded as MathML and are displayed in this HTML version using MathJax in order to improve their display. Uncheck the box to turn MathJax off. This feature requires Javascript. Click on a formula to zoom.
?Mathematical formulae have been encoded as MathML and are displayed in this HTML version using MathJax in order to improve their display. Uncheck the box to turn MathJax off. This feature requires Javascript. Click on a formula to zoom.Abstract
The financial institutions in emerging countries in general and Ethiopia in particular, where financial dualism is mostly practiced, strategic planning is critical to encounter the dynamic nature of the economic system. This study aims to examine the impact of strategic planning on the performance of public commercial banks in the context of Eastern Hararghe, Ethiopia. The study considered strategic planning perspectives: environmental scanning, strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation as explanatory variables whereas organizational performance was a dependent variable. A cross-sectional research design was used to investigate the relationship and impacts of the variables. A sample was drawn from managers and senior staff, who engage in planning and monitoring activities. Structured questionnaires were designed and administered based on a five-point Likert scale to gather the data. Descriptive statistics and econometric regression analysis techniques were employed after proper coding and testing of the reliability of the items. The findings revealed that strategic planning strongly and positively correlates with the bank’s overall performance. Finally, the study recommends that commercial banks should adopt strategic planning processes to enhance their overall performance.
REVIEWING EDITOR:
1. Introduction
Commercial banks play a pivotal role in driving economic growth and development by acting as a catalyst in the development process (Sime et al., Citation2020). They promote the habit of saving and mobilizing funds from numerous small households and businesses across a wide geographical area. Consequently, these mobilized funds are utilized for productive purposes (Isayas, Citation2022). In the current era of globalization, the business environment undergoes constant change and to deal with the challenges of the market, necessitating companies to evaluate both micro and macro environmental factors is needed to effectively address market challenges and achieve their objectives (Azeem et al., Citation2021). Bank performance evaluation is essential to provide information to understand the organization’s operational capacity and competitiveness (Mengistu, Citation2015).
In recent years, financial institutions have moved into greater competitiveness with a broad range of products and services (Liu, Citation2021). In response to the unpredicted market dynamism, commercial banks have shown a renewed interest in marketing their goods and services more effectively (Tien et al., Citation2021). Banks today are focused on becoming more competitive by adopting strategies that give them an advantage over others. To do this, it is compulsory to design practical strategies that help banks identify the appropriate marketing strategies to attract new customers and retain existing ones (Čater & Pučko, Citation2010; Chigamba & Fatoki, Citation2011). Otherwise, as the annual report of the Commercial Bank of Ethiopia disclosed the typical reasons for an inefficient organization and the failure of commercial banks in Ethiopia are attributed to inefficient use of resources, weak philosophy to adopt and utilize strategic planning practices, and lack of strategic roadmaps within the structure organization (Commercial Bank of Ethiopia [CBE], Citation2021).
However, each of these challenges can be effectively addressed through strategic planning (Obonyo & Arasa, Citation2012). To meet these challenges, banking sector administrations must adopt new approaches that strengthen competitive positions by increasing internal and external performance levels, particularly strategic performance. The outcome of several studies on the relevance of strategic planning to enhance the overall performance of organizations revealed that strategic planning has become a part of modern management tools and one of the most important approaches to improving the performance of organizations (Gomera et al., Citation2018; Omotayo et al., Citation2018; Rahman, Citation2019). On the contrary, some studies come up with different results, even contradicting each other such as (Ameur & Mhiri, Citation2013; Ongore & Kusa, Citation2013; Tesfaye & Shete, Citation2015).
Although several studies have examined the relationship between strategic planning and strategic performance, some gaps observed. Worth mentioning: Scolastica and Mboya (Citation2021), Nyanaro and Bett (Citation2018), Ndege and Ithara (Citation2014) examined the influence of strategic planning on bank financial performance in Kenya, Karsh et al. (Citation2020), examined the impact of strategic planning on the performance of bank employees in Palestine, and studies have also been conducted to assess the impact of strategic planning on management practices in the case of Berhan Bank in Ethiopia (Mesfin, Citation2021). All of them have taken financial performance and employee commitment as the performance indicator. However, this study considered additional performance indicators; such as efficiency, profitability, customer satisfaction, quality service, and market share by creating an index.
With this intention, the objective of the research presented in this article is to examine the impact of strategic planning on the performance of banks within Eastern Hararghe, Ethiopia. Eastern Hararghe, the focal point of this study, holds significance as a hub for large-volume trade, owing to its proximity to Dire Dawa, the nation’s sole import-export gateway. The banking sector in this region experiences substantial cash flow and active resource mobilization. Therefore, strategic management of business operations is imperative, alongside measuring the resultant impacts against the banks’ objectives.
To address this, the research aims to provide insights into the following key questions: (1) How and to what extent do the selected banks carry out their strategic planning? (2) What is the impact of strategic planning on a bank’s overall performance? (3) Which aspects of strategic planning do banks excel in, and where do they face weaknesses?
The outcomes of this research are expected to make a significant contribution by bridging the existing gaps in knowledge. Moreover, the findings are expected to be beneficial for administrators, business managers, and policymakers within banking sector. They can utilize this information to develop sustainable development programs and formulate intervention guidelines aimed at enhancing the effectiveness of banking strategies in meeting customer needs. Additionally, these findings will serve as a foundation for future research endeavors by scholars exploring similar topics in different contexts.
2. Literature review
2.1. Concept of strategy
The word ‘strategy’ is derived from the Greek word ‘strategos’, which means ‘the roles of a general’ (Chen & Mohamed, Citation2010). The Oxford Dictionary defines strategy as a design of action planned to attain a long-term or general goal. Originally, it was called business policy and has advanced substantially with the concentrated efforts of researchers and practitioners (Wheelen et al., Citation2017). It is not possible to have a strategic plan without a clear strategy. Rudd et al. (Citation2008) noted that, without a strategy, an organization is like a ship without a rudder. It goes round in circles and like a tramp, has no specific place to go.
2.2. The strategic planning process and its perspectives
According to Leebaw (Citation2019), in his work on participatory and ethical strategic planning states that strategic planning started in the 1940s and was popular in the 1960s and 1970s. However, the planning method was developed in the mid-1960s based on the ideas of American business schools. Strategic planning has received big attention from development, and business and public organizations as a means of crafting the vision, mission, and goals and includes methods for measuring progress (Obonyo & Arasa, Citation2012; Scolastica & Mboya, Citation2021). Strategic planning is a foundation for strategic management. It is a progressive exercise in which all level managers should be involved in the process (Boateng et al., Citation2015; Owolabi & Makinde, Citation2012).
The process of strategic planning is designed to achieve the firm’s vision and mission, which comprise four major perspectives: environmental analysis or scanning, strategic formulation, implementation, and adjustment/evaluation/control. These four basic elements interact with each other (Jenster & Søilen, Citation2013; Mesfin, Citation2021; Wheelen et al., Citation2017; Zafar et al., Citation2013) and they are also persuasive to the success or failure of the organization. Since the emphasis of the study is to investigate their impact on organizational performance the researchers have attempted to briefly discuss each of them as follows:
Environmental Scanning is also termed as situational analysis in the planning process where the first phase of strategic planning starts (Azhar et al., Citation2013). Both internal and external situations must be examined and communicated properly (Neolaka et al., Citation2023). Internal scanning conducts a SWOT analysis by focusing on the strengths and weaknesses of an organization while external evaluation conducts a SWOT analysis by concentrating on the opportunities and threats. Some of the main factors analyzed via internal scanning include resources and value-adding activities, the process used, and the organizational culture (Peng, Citation2021).
The business landscape entails three main factors: the micro, macro, and market environment. The micro-environment encompasses various aspects of the business including the corporate culture, goals, mission, vision, and departments. Organizational resources including expertise, human capital, and finances also constitute the micro-environment of a business (Pimentel et al., Citation2013). The macro-environment entails variables that are beyond the control of a business which are mainly analyzed through the PESTLE (Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, Technological, Legal, and Environment) tools (Cheong & Hoang, Citation2021). Some of these variables include economic issues such as inflation, demographic changes, and the emergence of new technology among other factors (Karami, Citation2012; Otieno et al., Citation2018). For this study purpose, respondents were asked whether the Bank scans its internal and external environment timely, which will have an impact on reducing risks and enhancing the probability of growth as Karami (Citation2012); and Mang’ana et al. (Citation2017) studied.
Strategy Formulation: is a process of determining the organization’s mission, goals, and objectives by crafting the appropriate strategy (Chungyas & Trinidad, Citation2022). According to Wickert et al. (Citation2021) states, strategy formulation guides top managers to define their destiny, and the means to accomplish these ends. According to Chaika (Citation2021), the industrial enterprise strategy formulation passes through three phases, whose terminology is often complicated: mission, vision, and objectives setting.
The mission statement of an organization represents the products and services that the organization aims to provide and the markets in which it intends to operate. Daft (Citation2021) and Rothaermel (Citation2017) postulate that effective communication of a mission statement is a valuable management tool for the company moving in the intended direction. The vision statement determines the future path of the organization, what the organization intends to reach, and the center it aims to achieve. The vision statement is important in an organization as an instruction towards the chosen direction (Obeidat et al., Citation2016). Strategic objectives are the results of planned activity that state what is to be accomplished by when and it should be quantified. It is also the organization’s performance targets that are planned to be achieved. Strategic objectives perform five functions in an organization namely: setting the responsibilities of managers, providing the framework for planning, using for the integration of organizational activities, and acting as a motivator to employees to work hard to achieve the targets are finally used to evaluate and control the performance of managers (Maina, Citation2020). For this study, researchers examine the existence of the organization’s mission, vision, and objectives vividly and who is involved in the preparation of the plan.
Strategy Implementation: refers to putting the strategy into action at all levels (Babafemi, Citation2015; Tawse & Tabesh, Citation2021). Organizational culture is the assumptions, beliefs, and values that members of a group in an organization are guided by based on the rules and regulations. Communication is an important element in the strategy implementation process and they are a major component that should be recognized (Hantiro & Maina, Citation2020). Kibe (Citation2014) concludes that proper communication in an organization is an integral part of strategy implementation due to its ability to provide information on time to the stakeholders hence empowering them to act in good time. Opano (Citation2013) opined that a ‘plan without effective and measurable implementation is no plan at all’ and those managers must combine sound strategy-making with good strategy execution for company performance. This study treats strategic implementation as interconnected with other perspectives in strategic planning.
Strategy Evaluation: is the systematic investigation carried out by an organization and it is a critical tool for managers to understand the reasons behind the failures and success of certain objectives, performance standards, and/or any other performance indicator (Mio et al., Citation2022). In this sense, evaluation is used as a strategic learning tool and has continued to play a role in strategy formulation and implementation. It played a vital role in protecting the business from collapse (Dubihlela & Sandada, Citation2014). Effective strategy evaluation must follow four steps: setting performance standards, actual performance measurement; variance analysis, and taking corrective action where necessary (Wickert et al., Citation2021). An organization that does not practice performance measurement would hardly deal efficiently and effectively with the uncertainty inherent to the environment, resulting in poor use of resources and consequently increasing the probability of failure.
2.3. Organizational performance and measurements
Armstrong and Taylor (Citation2014), defined performance as behavior that accomplishes results. The term performance refers to a set of outcomes produced during a certain period of their job time and does not refer to the traits, personal characteristics, or competencies of the performer. The evaluation of an employee’s performance reveals the contribution of an individual to the organization’s objectives (Toppo & Prusty, Citation2012). Therefore, performance is about job-related requirements expected of a worker and how well they translate into action. For this particular study purpose, the researchers preferred a performance in the banking industry to be expressed in a list of indicators; such as competitiveness, market share, profitability, customer satisfaction, quality service, efficiency, and many more as Galletta et al. (Citation2022).
Performance measurement systems are characterized as strategic expert systems by which organizations observe and measure their intangible performance elements in the form of qualitative and quantitative assessments (Fried, Citation2010). Performance measurement approaches can be divided into two types namely objective and subjective measurement (Elgestad Stjernfeldt et al., Citation2019). Objective measurement is based on financial measures whereas, subjective measurement is based on self-reported measures. Self-rating success (SRS) is one of the important approaches in subjective measures. SRS is obtained by asking the owners to rate their success on a scale from 1 (not very successful) to 5 (very successful). Subjective measures are preferred by some researchers because they capture a broad concept of a firm’s performance; On the other hand, it is difficult to obtain objective data for confidentiality reasons (Geng et al., Citation2015; Huseynov et al., Citation2017; Ismail et al., Citation2017; Sundvik, Citation2017). With this in mind, thus, this study used a subjective performance measurements approach to assess the performance of the bank from different dimensions. These performance indicators considered for this study are discussed as follows.
2.3.1. Employees’ commitment
A delightful atmosphere can be created by a satisfied employee in the organization, so employees will have better performance (Basalamah & As’ad, Citation2021; Sanjaghi, 2013). Dost et al. (Citation2011) investigated the impact of employee commitment on organizational performance and concluded that organizational performance can be enhanced by involving employees in decision-making. However, most of the past studies on employee commitment may not apply to the Ethiopian business environment. As such, it is pertinent to examine the role of employee commitment in achieving organizational performance in the Ethiopian context.
2.3.2. Operational efficiency
This is an economical usage of physical resources, systems, and structures. Operational efficiency minimizes waste and improves the ability of a business to provide products of good quality and render services of high standards to their clients (Upadhyay & Gupta, Citation2012). Operational efficiency can be measured both in quantitative and qualitative terms. Among these measures are financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal control, and business process, employees’ growth and development in the organization (Karimzadeh, Citation2012). Studies by Wasiuzzaman and Tarmizi (Citation2010) have found a positive impact and important operational efficiency in the profitability of commercial banks. The study, therefore, used this non-financial performance variable to measure the bank’s performance efficiency in the study environs.
2.3.3. Service quality
Service quality is an important aspect of measuring performance (Sangeetha & Mahalingam, Citation2011). Service quality is a method of managing a business and its processes to ensure and serve customer satisfaction, thereby increasing the competitiveness and effectiveness of the organization’s service. It is critical for the growth, development, and expansion of a business (Rahaman et al., Citation2011). In the service industry, quality of service is usually more important than in the manufacturing industry (Dadwal, Citation2017). As a result, it is vital to consider how service quality affects a company’s organizational performance in the context of the study environment.
2.3.4. Customer satisfaction
Customer Satisfaction is currently the main non-financial indicator that many organizations pay close attention to (Hallencreutz & Parmler, Citation2021; Ali et al., Citation2021). According to Ali and his colleagues, customer satisfaction and service quality have a positive and strong relationship. Customer satisfaction has developed into a crucial indicator of a company’s performance and, as a result, has drawn significant care in business-related literature. Son et al. (Citation2021) investigated into the relationship between worker and customer satisfaction. According to the research, customer satisfaction is influenced by employee satisfaction. Per se, it is relevant to look at this subjective measure variable in the context of the study area to achieve a business’ organizational performance.
2.3.5. Market share
Market Share is a significant non-financial performance metric that is calculated by comparing a bank’s total assets over a specific period to the total assets of the industry. Market share and bank profitability ought to be positively correlated. A large market share can produce a variety of goods to leverage market power, which can then set a high price and produce high profits. According to some studies, like Mirzaei et al. (Citation2013) and Sahile et al. (Citation2015), a high market share is correlated with bank profitability. Therefore, this variable was used in the study as a non-financial variable to assess its effect on the performance of the bank in the study area.
2.3.6. Bank’s profitability
Profitability is an important indicator of a bank’s performance. A bank’s operating performance, which includes profitability, is determined by its mission, regulations, and management actions (Guluma, Citation2021). Traditionally, profit maximization is the guiding principle of all profit-oriented business organizations. When the company’s management generates enough profits, shareholders and other investors are satisfied and the company is better able to meet the demands of other stakeholders. Profitability in banks becomes necessary for cost absorption, reinvestment, attracting further financing, maintaining public trust, and motivating (Ayalew, Citation2021). The study therefore used this variable as a non-financial variable to measure its influence on the bank’s overall performance.
In comparison to the rest of the world, Ethiopia’s financial system is sluggish. Given the increasing quantity of import-export trades and the complexities of the economic system around the globe, the current banking system is incapable of providing efficient and dependable services. As a result, the country has yet to fully reap the benefits of strategic management that uplifts the overall performance of the economy. Performance is a major axis for measuring the success and failure of organizations in their strategic goals and decisions in the strategic literature (Almansoori et al., Citation2021).
2.4. Conceptual framework
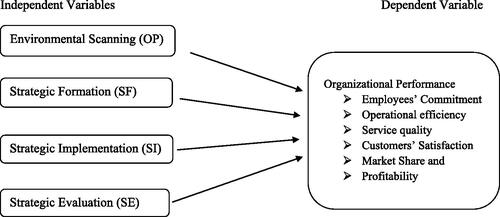
The variables that are employed in the study and how they interact are described by the conceptual framework (Yegzaw, Citation2022). The conceptual framework shown below illustrates how the strategic planning perspectives affect the overall performance of the bank under consideration. The conceptual model was created based on reviews of earlier works of literature to explain the relationships between the factors deemed essential to the literature part’s discussion
The conceptual framework used by Rahman (Citation2019) illustrates organizational performance from the perspectives of operational efficiency, financial turnover, and management system, while the performance indicators in our framework also include additional performance indicators like employees’ commitment, operational efficiency, service quality, customers’ satisfaction, market share, and profitability to meet the study’s goal.
Regarding the independent variables, various studies have been made by adopting one of the strategic planning views, as Okwemba and Njuguna (Citation2021a) did when they independently examined the impact of environmental scanning and strategic assessment on the organizational performance of Chemelil Sugar Company in Kisumu County, Kenya. Ngigi and Robert (Citation2023) made an effort in a different study to demonstrate the connection between organizational performance and strategic formation. While Mailu et al. (Citation2018) investigated how strategic implementation affects organizational performance. Four strategic planning perspectives on the organization’s overall performance, however, are included in our analysis. So, this is the gap that this study has filled. As a result, the research investigates the impact of strategic planning on the success of Ethiopian commercial banks at the Harar and Haramaya branches in question.
The following four research hypotheses were developed based on the research objective and research framework ():
Figure 1. Conceptual framework. Source: Developed from the evidence of researchers review and (Yegzaw, Citation2022, Rahman Citation2019).
H1: Environmental scanning has a positive and significant impact on the performance of selected commercial banks in Ethiopia,
H2: Strategic formulation has a positive and significant impact on the performance of selected commercial banks in Ethiopia,
H3: Strategy implementation has a positive and significant impact on the performance of selected commercial banks in Ethiopia, and
H4: Strategy evaluation has a positive and significant impact on the performance of selected commercial banks in Ethiopia.
3. Research methodology
3.1. Research design
To explore the connection between strategic planning and organizational performance within public commercial banks operating in Eastern Hararghe, Ethiopia, a cross-sectional research design was employed; specifically descriptive survey research design was used. The study targeted a population of 116 managers and senior staff across twelve branch offices situated in Harar city and Haramaya town. Accordingly, the respondents were selected proportionally from all branches to ensure the representativeness of the population using Yamane’s formula (as cited in Adam, Citation2020) outlined in Equation (1) below. Consequently, a total of 90 respondents were selected, consisting of 26 (29%) managers and 64 (71%) non-managerial senior staff who are actively involved in the planning process.
(1)
(1)
Where n is the sample size, N is the population size, and e is the margin of error (i.e. e = 5%).
To gather the data, a structured questionnaire was designed and administered based on a five-point Likert scale. From the total distributed questionnaire 86 were returned of which only 80 (93.02%) were complete and valid for analysis ().
Table 1. Target population, sample size, and return rate and validity of the questionnaires.
To ensure the validate of the instrument, pilot tests were conducted by selected respondents to assess their understanding and gather feedback. Following data collection, adjustments were made to the questionnaires based on the received responses.
3.1.1. Method of data analysis
The collected data was analyzed based on the objective of the study. Data clearing and editing were done before the final regression and testing of the result. The mean and standard deviations are computed for the descriptive analysis and presented in a tabular form. Whereas, for inferential statistics, Pearson correlation coefficient, ANOVA, and multiple linear regression procedures were computed to infer the relationship and impacts of strategic planning perspectives on organizational performance. A multiple linear regression model is specified in EquationEquation (2)(2)
(2) .
(2)
(2)
Where, OP (organization performance) is the dependent variable, and ES (environmental scanning), SF (strategic formation), SI (strategic implementation), and SE (strategic evaluation) are the independent variables. The coefficients are denoted by beta; is the constant confident and β1 to β4 are the marginal effects of Xi’s, which measures the change in the mean value of OP per unit change in their respective independent variables. ɛi is the stochastic term or the residual, that represents omitted variables, errors, and unexplained variables in the model.
According to Tutz (Citation2021) and Boone and Boone (Citation2012), the five-point Likert scale is considered an interval scale if it fulfills the normality test. Therefore, the researchers compute the average score of each variable in the analyses made on the base of composite scores of the items. Pearson correlation and multiple linear regressions were the main econometrics methods employed in this study to analyze the relationship between variables. Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) measures how strong is the correlation between two variables. Values of Pearson’s correlation coefficient are always between −1 and +1 (Bhattacherjee, Citation2012). Whereas, the regression analysis makes it possible to predict the variable based on other variables. The data was analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS-Ver 20) software.
4. Results, analysis and discussion
In light of the research objectives and research questions, this section aims to present the data analysis, research findings, and their interpretation. This investigation’s main goal is to determine how strategic planning affects the performance of public commercial banks. Inferential statistics are thus presented after descriptive statistics. Before analyzing the data, a reliability test was conducted under this part.
4.1. Reliability and internal validity testing
Cronbach’s Alpha scale was used to measure reliability. The values range between 0.00 (no consistency) to 1.00 (perfect consistency). According to Sekaran and Bougie (Citation2016), the alpha value is considered weak if it is less than 0.60, acceptable when the alpha score is between 0.60 and 0.70, good if it is between 0.70 and 0.80, and it is excellent if the value is greater than 0.80. As a result of this study, Cronbach’s alpha is 0.83 which means that 83% of the variance in the scores are reliable variance. Therefore, 17% is error variance. As exhibited in , the instrument used in this study is reliable for further analysis.
Table 2. Reliability test for strategic perspectives and performance.
Thus, the result of alpha indicates the data collection instrument is valid to assure internal validity, besides the sampling procedures applied.
4.2. Descriptive analysis of the strategic planning
The statistical descriptive analysis of respondents’ perception of organization performance across the four strategic planning perspectives was analyzed and presented in frequency .
Table 3. Respondents’ perception of banks’ performance across strategic planning perspectives.
Upon analyzing the overall perception of respondents towards strategic planning perspectives, the aggregate mean and standard deviation scores were determined to be 3.72 and 0.46, respectively. According to the five-point rating scale criterion, strategy formulation received the highest rating at a large extent, with a mean score of 3.96 and a standard deviation of0.644. Environmental scanning followed closely with a mean score of 3.80 and a standard deviation of 0.565, while strategy evaluation obtained a mean score of 3.78 with a standard deviation of 0.746. Strategy implementation received the lowest rating, with a mean score of 3.36 and a standard deviation of 0.765.
This suggests that the selected banks placed significant emphasis on strategy formulation, indicating clearly defined and documented missions, visions, and goals. Environmental scanning and strategy evaluation were moderately emphasized, ranking second and third, respectively. As a profit-oriented public enterprise, the bank has a mechanism to scan the external threats and opportunities and analyze them to make an informed decision. In terms of evaluation, the firm has a culture of measuring performance on a regular basis, yearly. However, they were relatively weak in comparing results against objectives and identifying reasons for variations.
The results also revealed that strategy implementation received less emphasis, suggesting a need for the organization to focus more on executing the plan comprehensively. Hence, the bank is expected to do a lot by focusing on all aspects of its performance, specifically from the strategy implementation perspective. The study confirms a positive relationship between strategic planning perspectives and performance, aligning with previous findings by Mang’ana et al. (Citation2017), Nyagaki (Citation2022), Okwemba et al. (Citation2021a), and Onikoyi et al. (Citation2022).
Furthermore, descriptive analysis found that the standard deviations of the strategic planning dimensions had the lowest coefficient of variation, indicating that respondents were similar in their perceptions and pay close attention to the variables. This suggests that the effects of strategic planning on bank performance followed a normal distribution, indicating organizational satisfaction among respondents.
4.3. Descriptive analysis of the status of strategic performance
This study evaluates the current level of performance in CBE through the lens of strategic planning, considering six key elements outlined in .
Table 4. Descriptive analysis for constructed variables and organizational performance.
These elements include employees’ commitment, operational efficiency, service quality, customer satisfaction, market share, and organizational profitability.
An overall mean and standard deviation of (M = 3.68, SD = 0.464) suggest that the constructed performance parameters significantly contribute to the organizational performance of banks. Among these parameters, profitability and customer satisfaction received the highest ratings, with mean of (M = 3.88, SD = 0.886) and (M = 3.84, SD = 0.848), respectively. This indicates that the selected banks prioritize profitability and customer satisfaction. These findings align with the bank’s annual report of 2020/21, which highlights the achievement of the highest profit (USD 357.41 million) before tax in the history of CBE (2020/21). In addition, this result indicates that respondents were less varied in their opinion of the responses given under organizational performance parameters as their standard deviation spread ranged from 0.848 to 0.898. Hence, the finding shown in , is consistent with the literature reviewed. To deduce the result of the study inferential statistics are computed hereunder.
4.4. Correlation analysis
As depicted in , all strategic perspectives are significantly correlated with the organization’s performance. As compared to others, strategy formation is strongly correlated (r = 0.742), followed by environmental scanning (r = 0.665), strategy evaluation (r = 0.631), and strategy implementation (r = 0.454). As the intercorrelation shows, the independent variables have a loose and significant correlation except for the correlation between ES and SI. This is one indication that multicollinearity does not exist. This finding contrasts with the results of Boateng et al. (Citation2015), whose finding shows a weak but significant correlation between the degrees of strategic planning process formality and their institutional performance in Ghana private universities In our study, however, the correlation between strategic planning and organizational performance is notably higher and statistically significant. Besides the correlation test for multicollinearity, VIF (Variance Inflation Factor) determines the strength of correlation between the independent variables, it is predicted by taking the variable and regressing it against every other variable. The VIF score of an independent variable represents how well the variable is explained by other independent variables. The recommended minimum standard for VIF is less than ten and tolerance is less than one.
Table 5. Correlation matrix.
This suggests that there is no multicollinearity or that the variables are not explained by other factors. Therefore, regression can be made without removing any of our explanatory variables. As a result, shows VIF value is very low (i.e. 1.35), this suggests that there is no multicollinearity or that the variables are not explained by other factors. Therefore, regression can be made without removing any of our explanatory variables.
Table 6. Co-linearity statistics.
Before the regression analysis, the presence of heteroscedasticity was checked using the Breusch-Pagan test. It is used to check whether the variance of the residual from the predicted value is dependent on the values of the independent variables.
From , since the test statistic has a p-value above an appropriate threshold (p < 0.05) we do not have evidence to reject the null hypothesis that is a constant variance. This implies that our data is free of heteroscedasticity problems or that the variables have a constant variance from the stochastic term.
Table 7. Breusch-Pagan/Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity.
4.5. Regression analysis, coefficient determination and hypotheses testing
A multiple linear regression model was applied to determine the relation between the coefficient of strategic planning perspectives and organizational performance.
Results on the goodness of fit are presented in . The findings designate that the study factors or the overall strategic planning perspectives were fittingly enlightening organizational performance. This deduction is reinforced by the finding of R square of 0.779, which shows that the explanatory variables jointly explain 77.9% of organizational performance, with the remaining 22.1% stated by variables not included in the model.
Table 8. Goodness of fit/model fitness summary.
The multiple regression of OP on ES, SF, SI, and SE () confirms the model is statistically significant as the value of significance was less than 5% (α = 0.05). The result revealed that strategic planning has a positive effect on organizational performance. From the table, the coefficients indicate there is a direct relationship between the dependent and independent variables.
Table 9. Relation between coefficient of strategic planning perspectives & bank’s performance.
The unstandardized coefficient constant beta () indicates that even if all the dependent variables are excluded or kept constant the organization’s performance will change by 0.732. The model shows that with a unit increase in the degree of ES, OP was improved by 25.5 percent, holding all other independent variables constant. ES also accounts for 4.7 percent of the variation in OP. This implies that a unit decrease in the degree of ES (assessing the traits and opportunity) might have resulted in a decrease in the OP by 25.5 percent. This finding is in agreement with the results of Onikoyi et al. (Citation2022); and Mang’ana et al. (Citation2017) who studied the relationship and effect of environmental scanning of SP on OP.
Regarding the SF, SI, and SE their corresponding coefficient value is 0.274, 0.105, 0.139, respectively. They all have a positive relationship with the OP as the ES does. This result can be interpreted as a one percent change in SF, SI, and SE, keeping other variables constant, with results of 27.4, 10.5, and 13.9% of the variation/change in commercial bank’s performance respectively. Each of those dependent variables also accounts for 4.3, 3.2, and 3.6, percent of the variation in OP respectively. This implies that a unit decrease in the degree of SF for example might have resulted in a fall in the OP by 27.4 percent. There was a substantial correlation between strategy formulation and organizational performance, according to the results of the multiple linear regression. These findings are consistent with those of other previously conducted studies, including those conducted by Owich et al. (Citation2018); Maina (Citation2020); Ngigi and Robert (Citation2023); Baroto et al. (Citation2014); Al Dhaheri et al. (Citation2020). Following the analysis result from , the linear regression was derived as:
(3)
(3)
A plethora of literature also undoubtedly supports the positive impact of strategy implementation on organizational performance, as demonstrated by Mailu et al. (Citation2018); Mathore (Citation2016); Khoshtaria (Citation2018); Onyegbula et al. (Citation2023), Njagi and Kombo (Citation2014). Similarly, this research revealed the positive and statistically significant impact of implementation on organizational performance. Concerning strategy evaluation, previous studies have revealed the positive impact of strategy evaluation on organizational performance (Okwemba & Njuguna, Citation2021b). In line with the outcomes of the previous research, this study also indicates the positive impact of strategy evaluation on the performance of commercial banks in Ethiopia.
In light of this, the hypothesis that all explanatory variables have an impact on organizational performance is accepted. This implies ES, SF, SI, and SE, have a positive and significant impact on the performance of selected commercial banks in Ethiopia. When the parameters’ coefficients are compared, the effect of SF and ES is higher; whereas the effect of SI and SE are relatively low. This may be due to a weak connection between day-to-day operations and the long-term strategic activities of the organization. The bank evaluates the environment and formulates the plan but when it comes to implementation it reverts slightly to the level that was anticipated.
5. Conclusion
The results of the correlation analysis reveal a positive and significant relationship between all independent variables with the dependent one., This indicates that a change in one of the strategic planning perspectives positively influences the other dimensions of strategic planning, subsequently enhance organizational performance.
Based on the findings related to strategic planning and organizational performance, it can be inferred that public commercial banks in the study area effectively engage in strategic planning. This, in turn, leads to a positive impact on organizational performance by fostering workers’ commitment, enhancing customer satisfaction, increasing efficiency, and increasing market share. However, it is noted that the implementation of strategies was rated relatively weak compared to environmental scanning, formulation, and performance evaluation. From an overall assessment of organizational performance, it is evident there is room for improvement within the commercial bank. There is a need for greater emphasis on translating strategic plans into actionable steps for implementation. This underscores the importance for commercial banks to align their implementation efforts with the strategic vision, mission, and objectives of the organization.
5.1. Limitations and policy implications for further research
Despite the encouraging findings, this study has certain drawbacks. Firstly, it focuses solely on the impact of strategic planning on organizational performance, neglecting other crucial factors such as capital structures, liquidity, organizational structure, human capital, infrastructure, technology, and corporate governance system, all of which significantly influence a Bank’s performance. Secondly, the study relies on primary data gathered from a limited number of branches of CBE. Utilizing long time-series data and employing both qualitative and quantitative analysis techniques could have provided more comprehensive insights. Lastly, the study’s geographical focus on Eastern Hararghe, while a busiest commercial areas in the country may not represent the diversity of economic activities in other regions. Thus, researchers are encouraged other scholars to conduct broad-ranging research that takes into account private financial institutions, more variables, and different techniques of analysis to embrace multidimensional perspectives.
Policymakers should recognize the crucial role of strategic planning on the organizational performance measured in terms of boosted employee commitment, efficient utilization of resources, quality service provision, profitability, rising customer satisfaction, and market share growth. To achieve this, policymakers must prioritize service excellence aligned with the organization’s vision and mission. This can be done via proper analysis of the external environment, setting a genuine plan, effective implementation of the plan, and timely evaluation of the outcome.
Author contribution
The authors affirm that they each contributed equally to this research.
Likert scale Questioner_SPon OP.docx
Download MS Word (23.5 KB)Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate all of the feedback and recommendations provided by the reviewers. For this study, the authors were not given any direct funding.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Data availability statement
Available on request.
Additional information
Notes on contributors

Frezer Tilahun Tefera
Frezer Tilahun Tefera (Ph.D. student) is an economics lecturer at Haramaya University in Ethiopia. Studied for his master’s degree in development management at the Ruhr University Bochum, Germany. He has participated in several self-development and professional training courses. He has gained extensive experience working for the Federal Government of Ethiopia at the Ministry of Finance and Economic Development in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. His research interests include economic development management, public finance, and trade. He has published three scientific articles in renowned journals. He engaged in volunteer work and documentaries in his free time.

Seifemichael Abebe
Seifemichael Abebe has studied Economics (BA) and Agricultural Economics (MSc) at Haramaya University, Ethiopia. He has substantial experience with government policies and strategies for nearly three decades. Furthermore, experienced in the development, implementation, and management frameworks of strategic plans, programs, and research projects and capable of translating strategic goals into clear operational plans to measurable results with Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) systems using Balanced Score Card (BSC) methods.
References
- Adam, A. M. (2020). Sample size determination in survey research. Journal of Scientific Research and Reports, 26(5), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.9734/jsrr/2020/v26i530263
- Al Dhaheri, F., Ameen, A., & Isaac, O. (2020). The influence of strategy formulation (vision, mission, and goals) on the organizational operations. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(17), 1932–1941.
- Ali, B. J., Saleh, P. F., Akoi, S., Abdulrahman, A. A., Muhamed, A. S., Noori, H. N., & Anwar, G. (2021, May). Impact of service quality on customer satisfaction: Case study at online meeting platforms. International Journal of Engineering, Business and Management, 5(2), 65–77. https://doi.org/10.22161/ijebm.5.2.6
- Almansoori, M. R. M. A., Al-Tahitah, A. N. A., & Battour, M. M. K. M. (2021). The impact of strategic planning on the performance of economic governmental organizations: The moderating role of organizational leadership and sustainability. International Journal of Contemporary Management and Information Technology, 1(6), 1–8.
- Ameur, I. G. B., & Mhiri, S. M. (2013). Explanatory factors of bank performance evidence from Tunisia. International Journal, 2(1), 1–11.
- Armstrong, M., & Taylor, S. (2014). Handbook of human resource management practice.13th ed. Kogan Page Limited.
- Ayalew, Z. A. (2021). Capital structure and profitability: Panel data evidence of private banks in Ethiopia. Cogent Economics & Finance, 9(1), 1953736. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2021.1953736
- Azeem, M., Ahmed, M., Haider, S., & Sajjad, M. (2021). Expanding competitive advantage through organizational culture, knowledge sharing, and organizational innovation. Technology in Society, 66, 101635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101635
- Azhar, A., Ikram, S., Rashid, S., & Saqib, S. (2013). The role of leadership in strategy formulation and implementation. Studies, 1(2) 32–38.
- Babafemi, I. D. (2015). Corporate strategy, planning, and performance evaluation: A survey of the literature. Journal of Management Policies and Practices, 3(1), 43–49. https://doi.org/10.15640/jmpp.v3n1a6
- Baroto, M. B., Arvand, N., & Ahmad, F. S. (2014). Effective strategy implementation. Journal of Advanced Management Science, 2(1), 50–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2019.1594756
- Basalamah, M. S. A., & As’ad, A. (2021). The role of work motivation and work environment in improving job satisfaction. Golden Ratio of Human Resource Management, 1(2), 94–103. https://doi.org/10.52970/grhrm.v1i2.54
- Bhattacherjee, A. (2012). Social science research: Principles, methods, and practices. University of South Florida.
- Boateng, P. A., Ganu, J., & Amponsah, E. B. (2015). Strategic planning process formality and institutional performance. European Journal of Business and Management, 7(20), 132–142.
- Boone, H. N., Jr., & Boone, D. A. (2012). Analyzing Likert data. Journal of Extension, 50(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.34068/joe.50.02.48
- Čater, T., & Pučko, D. (2010). Factors of effective strategy implementation: Empirical evidence from Slovenian business practice. Journal of East European Management Studies, 15(3), 207–236. https://doi.org/10.5771/0949-6181-2010-3-207
- Commercial Bank of Ethiopia [CBE]. (2021). Commercial Bank of Ethiopia: Annual report 2020/21. Retrieved in 2023, from ttps://combanketh.et/en/publications/.
- Chaika, N. (2021). Formation of development strategy for industrial enterprise. Quality-Access to Success, 22(180), p. 20.
- Chen, L., & Mohamed, S. (2010). The strategic importance of tacit knowledge management activities in construction. Construction Innovation, 10(2), 138–163. https://doi.org/10.1108/14714171011037165
- Cheong, C., & Hoang, H. V. (2021). Macroeconomic factors or firm-specific factors? An examination of the impact on corporate profitability before, during, and after the global financial crisis. Cogent Economics & Finance, 9(1), 1959703. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2021.1959703
- Chigamba, C., & Fatoki, O. (2011). Factors influencing the choice of commercial banks by university students in South Africa. International Journal of Business and Management, 6(6), 66. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v6n6p66
- Chungyas, J. I., & Trinidad, F. L. (2022). Strategic management practices and business performance of cooperatives in Ifugao, Philippines: basis for strategic planning model. International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, 4(2), 84–104. https://doi.org/10.51594/ijmer.v4i2.293
- Dadwal, S. S. (2017). Service sector and antecedents of marketing strategies for emerging markets: A case of Indian market. In Promotional strategies and new service opportunities in emerging economies (pp. 1–31). IGI Global.
- Daft, R. L. (2021). Management. Cengage Learning, 2021(5), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.12968/S2514-9768(22)90455-7
- Dost, M. K. B., Ahmed, Z., Shafi, N., & Shaheen, W. A. (2011). Impact of employee commitment on organizational performance. Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 1(3), 87–98.
- Dubihlela, J., & Sandada, M. (2014). Impact of strategic planning on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) performance: The role of employee participation, implementation incentives, and evaluation and control. Journal of Economics, 5(1), 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/09765239.2014.11884983
- Elgestad Stjernfeldt, P., Sjögren, P., Wårdh, I., & Boström, A. M. (2019). A systematic review of measurement properties of methods for objectively assessing masticatory performance. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research, 5(1), 76–104. https://doi.org/10.1002/cre2.154
- Fried, A. (2010). Performance measurement systems and their relation to strategic learning: A case study in a software-developing organization. Critical Perspectives on Accounting, 21(2), 118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2009.08.007
- Galletta, S., Mazzù, S., Naciti, V., & Vermiglio, C. (2022). Gender diversity and sustainability performance in the banking industry. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 29(1), 161–174. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2191
- Geng, R., Bose, I., & Chen, X. (2015). Prediction of financial distress: An empirical study of listed Chinese companies using data mining. European Journal of Operational Research, 241(1), 236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2014.08.016
- Gomera, S., Chinyamurindi, W. T., & Mishi, S. (2018). Relationship between strategic planning and financial performance: The case of small, micro and medium-scale businesses in the Buffalo City Metropolitan. South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences, 21(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajems.v21i1.1634
- Guluma, T. F. (2021). The impact of corporate governance measures on firm performance: The influences of managerial overconfidence. Future Business Journal, 7(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-021-00093-6
- Hallencreutz, J., & Parmler, J. (2021). Important drivers for customer satisfaction–from product focus to image and service quality. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 32(5–6), 501–510.
- Hantiro, S. B., & Maina, R. (2020). Strategy implementation and performance of Tana River County government, Kenya. Journal of Strategic Management, 4(1), 16–34.
- Huseynov, F., Sardarli, S., & Zhang, W. (2017). Does index addition affect corporate tax avoidance? Journal of Corporate Finance, 43, 241–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2017.01.008
- Isayas, Y. N. (2022). Determinants of banks’ profitability: Empirical evidence from banks in Ethiopia. Cogent Economics & Finance, 10(1), 2031433. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2022.2031433
- Ismail, W. S. W., Ali, A., & Rashid, N. M. N. N. M. (2017). Does adoption of CAIS differentiate the SMEs performance: Evidence in Malaysia. World Applied Sciences Journal, 35(9), 1981–1985.
- Jenster, P., & Søilen, K. S. (2013). The relationship between strategic planning and company performance–a Chinese perspective. Journal of Intelligence Studies in Business, 3(1), 15–30. https://doi.org/10.37380/jisib.v3i1.54
- Karami, A. (2012). An investigation on environmental scanning and growth strategy in high tech small and medium-sized enterprises. Paper submitted to the High Technology Small Firms Conference., 21st to 23rd May 2008, University of Twente (Downloaded on 7th March).
- Karimzadeh, M. (2012). Efficiency analysis by using data envelop analysis model: Evidence from Indian banks. International Journal of Finance, Insurance and Risk Management, 2(3), 228–237.
- Karsh, A., Sharif. M., & Abu Khader, S. R. (2020). Strategic planning impact on banks employees’ performance: Palestine. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 29(9), 4640–4652.
- Khoshtaria, T. (2018). The impact of strategic planning on organizational performance through strategy implementation. Globalization & Business, 4(5), 84–89.
- Kibe, C. W. (2014). Effects of communication strategies on organizational performance: A case study of Kenya Ports Authority. European Journal of Business and Management, 6(11), 6–10.
- Leebaw, D. (2019). Participatory and ethical strategic planning: What academic libraries can learn from critical management studies. Library Trends, 68(2), 110–129. https://doi.org/10.1353/lib.2019.0033
- Liu, M. X. (2021). Stay competitive in the digital age: the future of banks. International Monetary Fund.
- Mailu, R. N., Ntale, J. F., & Ngui, T. K. (2018). Strategy implementation and organizational performance in the pharmaceutical industry in Kenya. International Academic Journal of Human Resource and Business Administration, 3(2), 33–47.
- Maina, P. N. (2020). Influence of strategy formulation on the performance of state corporations in Kenya [Doctoral dissertation]. KeMU.
- Mang’ana, R. O., Rotich, G., Hassan, G., & Orwa, G. (2017). Influence of environmental scanning on the performance of Matatu savings and credit cooperatives in Kenya. Journal of Business and Strategic Management, 2(4), 32–53. https://doi.org/10.47941/jbsm.198
- Mathore, J. (2016). Effect of strategy implementation on organization performance: A case study of diamond trust bank [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Nairobi.
- Mengistu, M. M. (2015). Evaluation of the financial performance of the banking sector in Ethiopia: The case of Zemen Bank. Global Journal of Management and Business Research & Finance, 15(9), 88–100.
- Mesfin, M. (2021). Assessment of strategic planning and management practice in Berhan Bank Sc. [Doctoral dissertation]. St. Mary’s university.
- Mio, C., Costantini, A., & Panfilo, S. (2022). Performance measurement tools for sustainable business: A systematic literature review on the sustainability balanced scorecard use. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 29(2), 367–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2206
- Mirzaei, A., Moore, T., & Liu, G. (2013). Does market structure matter on banks’ profitability and stability? Emerging vs. advanced economies. Journal of Banking & Finance, 37(8), 2920–2937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2013.04.031
- Ndege, N. M., & Ithara, G. (2014). The influence of strategic planning on performance of commercial banks in Kenya: A case study of Barclays Bank of Kenya Ltd. International Journal of Social Sciences and Entrepreneurship, 1(12), 45–65.
- Neolaka, A. M. Y., Faulina, M., Akromah, P., Novilasari, T. A., & Napitupulu, R. H. M. (2023). Marketing strategy using SWOT analysis (case study: Stima Immi). Jurnal Ekonomi, 12(02), 1650–1659.
- Ngigi, K. D., & Robert, A. (2023). Influence of strategy formulation on the performance of catholic parishes in Kenya. Journal of African Studies and Development, 15(1), 1–13.
- Njagi, L., & Kombo, H. (2014). Effect of strategy implementation on performance of commercial banks in Kenya. European Journal of Business and Management, 6(13), 62–67.
- Nyagaki, B. K. (2022). Influence of strategic management practices on organisational performance. A survey of commercial based parastatals in Kenya [Doctoral Dissertation]. KeMU.
- Nyanaro, N. N., & Bett, S. (2018). Influence of strategic planning on performance of commercial banks in Kenya: Case of Barclays Bank of Kenya. International Academic Journal of Human Resource and Business Administration, 3(2), 235–255.
- Obeidat, B. Y., Hashem, L., Alansari, I., Tarhini, A., & Al-Salti, Z. (2016). The effect of knowledge management uses on total quality management practices: A theoretical perspective. Journal of Management and Strategy, 7(4), 18–29. https://doi.org/10.5430/jms.v7n4p18
- Obonyo, P., & Arasa, R. (2012). The relationship between strategic planning and firm performance. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 2(2)
- Okwemba, J. A., & Njuguna, N. (2021a). Effect of environmental scanning on performance of Chemelil Sugar Company in Kisumu County, Kenya. Journal of Strategic Management, 5(4), 57–69. https://doi.org/10.53819/81018102t5037
- Okwemba, J. A., & Njuguna, N. (2021b). Effect of strategy evaluation on performance of Chemelil Sugar Company in Kisumu County, Kenya. African Journal of Emerging Issues, 3(11), 1–15.
- Omotayo, O., Michael, O., & Andre, A. (2018). Strategic planning and corporate performance in the Nigerian banking industry. Asian Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting, 7(2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.9734/AJEBA/2018/36118
- Ongore, V. O., & Kusa, G. B. (2013). Determinants of financial performance of commercial banks in Kenya. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 3(1), 237–252.
- Onikoyi, I. A., Odumeru, J. A., Tajudeen, W. O., & Odeh, C. D. (2022). Environmental scanning and organisational performance in Unilever Nigeria PLC. The Journal of Accounting and Management, 12(3), 132–145.
- Onyegbula, E. F., Nwoye, M. I., & Daniel, C. O. (2023). Impact of strategy implementation on the performance of regulatory and supervisory agencies in the financial services sector in Nigeria. Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies, 11(02), 298–315. https://doi.org/10.4236/jhrss.2023.112019
- Opano, J. O. (2013). Strategic planning and implementation practices at the Kisii county government in Kenya [Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi.
- Otieno, D. O., Namusonge, G. S., & Mugambi, F. (2018). Effect of strategic planning on the financial performance of small and medium-sized enterprises in the professional service sector in Kenya. International Journal of Arts and Commerce, 7(6), 57–71.
- Owich, S., Katuse, P., & Ngari, J. (2018). The influence of strategy formulation on organizational performance of companies listed at Nairobi Securities Exchange. International Journal of Novel Research in Marketing Management and Economics, 5(2), 33–49.
- Owolabi, S. A., & Makinde, O. G. (2012). The effects of strategic planning on corporate performance in university education: A study of Babcock University. Kuwait Chapter of Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 2(4), 1–18.
- Peng, M. W. (2021). Global strategy. Cengage Learning.
- Pimentel, A. C. M., Spínola, M., & Moraes, R. D. O. (2013). Environmental scanning and SMEs strategies: A case study. Proceedings. Challenges for Sustainable Operations. S.l: ABEPRO.
- Rahaman, M. M., Abdullah, M., & Rahman, A. (2011). Measuring service quality using SERVQUAL model: A study on PCBs (Private Commercial Banks) in Bangladesh. Business Management Dynamics, 1(1), 1–11.
- Rahman, A. A. A. A. (2019). The impact of strategic planning on enhancing the strategic performance of banks: Evidence from Bahrain. Banks and Bank Systems, 14(2), 140.
- Rothaermel, F. T. (2017). Competitive advantage, firm performance, and business models. In Strategic Management (3rd ed., pp. 140–171). New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill Education.
- Rudd, J. M., Greenley, G. E., Beatson, A. T., & Lings, I. N. (2008). Strategic planning and performance: Extending the debate. Journal of Business Research, 61(2), 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2007.06.014
- Sahile, S. W. G., Tarus, D. K., & Cheruiyot, T. K. (2015). Market structure-performance hypothesis in Kenyan banking industry. International Journal of Emerging Markets, 10(4), 697–710. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJoEM-12-2012-0178
- Sahul Hamid, F. (2017). The effect of market structure on banks’ profitability and stability: Evidence from ASEAN-5 countries. International Economic Journal, 31(4), 578–598. https://doi.org/10.1080/10168737.2017.1408668
- Sangeetha, J., & Mahalingam, S. (2011). Service quality models in banking: a review. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 4(1), 83–103. https://doi.org/10.1108/17538391111122221
- Ramezan, M., Sanjaghi, M. E., & Rahimian Kalateh Baly, H. (2013). Organizational change capacity and organizational performance: An empirical analysis on an innovative industry. Journal of Knowledge-Based Innovation in China, 5(3), 188–212. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKIC-07-2013-0012
- Scolastica, C., & Mboya, M. A. (2021). Influence of strategic planning on financial performance of listed commercial banks in Kenya, 9(2), 92–115.
- Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building approach. John Wiley & Sons.
- Sime, K., Lemmie, K., & Gutu, E. (2020). The determinant of commercial banks’ financial performance in Ethiopia. Jurnal Perspektif Pembiayaan Dan Pembangunan Daerah, 8(1), 31–40. https://doi.org/10.22437/ppd.v8i1.8682
- Son, J. H., Kim, J. H., & Kim, G. J. (2021). Does employee satisfaction influence customer satisfaction? Assessing coffee shops through the service profit chain model. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 94, 102866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102866
- Sundvik, D. (2017). Tax-induced fiscal year extension and earnings management. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 18(3), 356–374. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAAR-06-2015-0051
- Tawse, A., & Tabesh, P. (2021). Strategy implementation: A review and an introductory framework. European Management Journal, 39(1), 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2020.09.005
- Tesfaye, R., & Shete, M. (2015). Determinants of the financial performance of a private commercial bank in Ethiopia. Journal of Business and Administrative Studies, 7(2), 1–30.
- Tien, N. H., Son, T. H., Anh, D. B. H., & Duc, N. M. (2021). Factors affecting customer satisfaction on service quality at joint stock commercial banks in Vietnam. Journal of Critical Reviews, 8(2), 605–617.
- Toppo, L., & Prusty, T. (2012). From performance appraisal to performance management. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 3(5), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.9790/487X-0350106
- Tutz, G. (2021). Hierarchical models for the analysis of Likert scales in regression and item response analysis. International Statistical Review, 89(1), 18–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/insr.12396
- Upadhyay, D., & Gupta, A. (2012). Efficacy of performance management system: An empirical study at ICICI Bank. International Journal of Advanced Research in Management and Social Sciences, 1(3), 216–225.
- Wasiuzzaman, S., & Tarmizi, H. A. B. A. (2010). Profitability of Islamic banks in Malaysia: an empirical analysis. Journal of Islamic Economics, Banking and Finance, 6(4), 53–68.
- Wheelen, T. L., Hunger, J. D., Hoffman, A. N., & Bamford, C. E. (2017). Strategic management and business policy (vol. 55). Pearson.
- Wickert, C., Post, C., Doh, J. P., Prescott, J. E., & Prencipe, A. (2021). Management research that makes a difference: Broadening the meaning of impact. Journal of Management Studies, 58(2), 297–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12666
- Yegzaw, D. A. (2022). A framework for effective strategy implementation: A resource-capability approach: The case of commercial banks in Ethiopia [Doctoral dissertation]. University of South Africa.
- Zafar, F., Babar, S., & Abbas, H. (2013). The art of strategic management key to success in the corporate sector. European Journal of Research and Reflection in Management Sciences, 1(1), 15–24.

