Figures & data
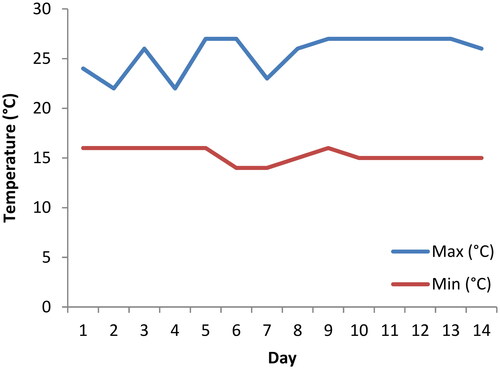
Figure 2. Cumulative mortality of Eristalis tenax after exposure to imidacloprid after 3, 7 and 14 days, (a) indoors and (b) outdoors. The data are expressed as mean ± SE. Mortality data in the treatments were converted into percentage mortality based on mortality data from the respective controls. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between the treatments at p ˂ 0.05.
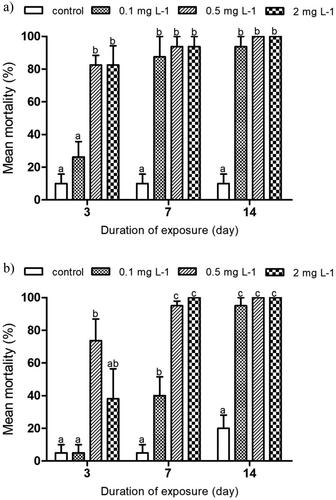
Figure 3. Activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the hoverfly larvae of Eristalis tenax exposed to imidacloprid contaminated substrate for 3, 7 and 14 days, a) indoors and b) outdoors. Data is expressed as mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments at p ˂ 0.05.
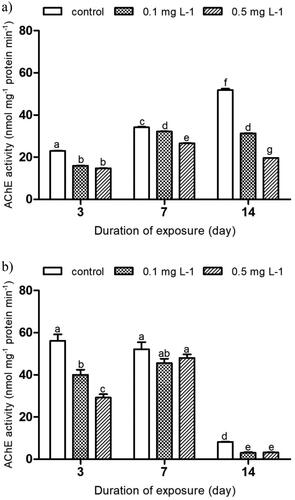
Figure 4. Activity of catalase (CAT) in the hoverfly larvae of Eristalis tenax exposed to imidacloprid contaminated substrate for 3, 7 and 14 days, a) indoors and b) outdoors. Data is expressed as mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments at p ˂ 0.05.
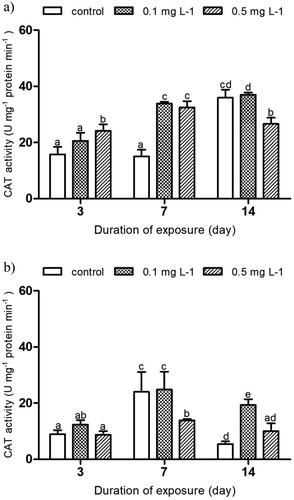
Table 1. Published chronic imidacloprid median lethal (LC50) and effective (EC50) concentrations (mg L−1) for the Diptera species tested in the present and previous studies.
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.