Figures & data
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified DENV domain III.1–4 Fc fusion proteins (Avi-tagged) and the DIII.3-Fc-Avi mutant bearing the point mutation K310E. All five fusion proteins were readily purified on protein G column and analyzed under reducing conditions. M, Protein Marker.
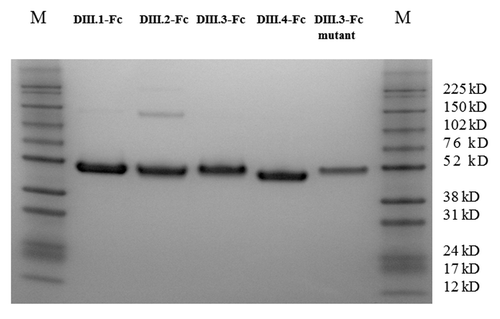
Figure 2. Enrichment of yeast display antibodies with specific binding to biotinylated domain III.3-Fc after three rounds of AutoMACS-based sorting of the naïve library against biotinylated domain III.3-Fc. Antibody expression on the yeast cell surface was detected with mouse anti-c-Myc antibody and Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody as the secondary antibody; binding of the yeast surface displayed antibody to the biotinylated antigen was detected via R-Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated streptavidin. (A) The original naïve yeast library before sorting and (B) the yeast pool after three rounds of sorting was incubated with 1 μg/ml of biotinylated domain III.3-Fc and 2 μg/ml of mouse anti-c-Myc antibody before staining with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated secondary antibody and PE-conjugated streptavidin.
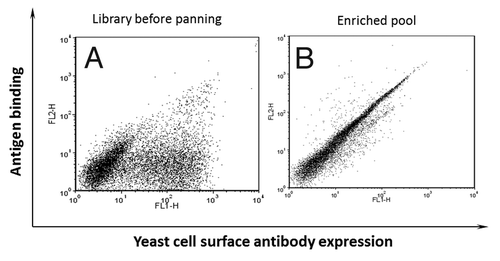
Figure 3. Competitive sorting of enriched yeast pool using the domain III.3 mutant K310E as a competitor. Sorting gate was set to sort out the cells that could not be competed by an excessive amount of the mutant.
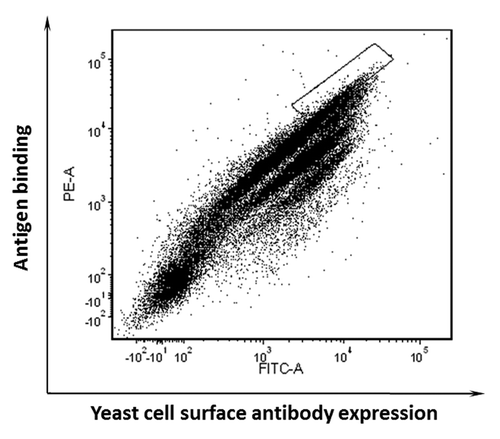
Figure 4. Purification and ELISA binding assay of isolated domain III specific binders D6 and D7. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of D6 and D7 scFv-Fc fusion proteins. Lane 1-D6 scFv-Fc; Lane 2-D7 scFv-Fc. ELISA binding assessment of (B) D6 scFv-Fc and (C) D7 scFv-Fc to c-Myc tagged domain III.1–4-Fc proteins. D6 scFv-Fc and D7 scFv-Fc were each coated on plate at 2 μg/ml; DENV domain III.1–4-c-Myc tag was added as antigens and binding was detected via mouse anti-c-Myc-HRP. (D) Competition ELISA showing the binding epitopes of D6 scFv-Fc and D7 scFv-Fc overlap. D6 scFv-Fc was coated on plate, serially diluted c-Myc tagged domain III.3-Fc only or mixed with a constant amount of competitor (K310E mutant or D7 scFv-Fc) was added to each well and binding of the domain III.3-Fc was detected by mouse anti-c-Myc-HRP antibody.
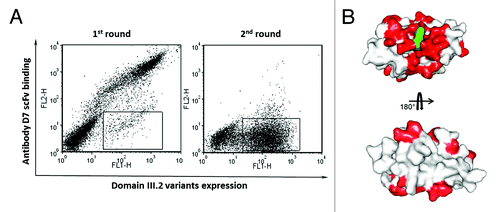
Figure 5. Epitope mapping of binder D7 on DENV envelope protein domain III.2. (A) Sorting of the yeast display domain III.2 mutant library. Expression of DENV domain III.2 variants on the yeast cell surfaces was detected with mouse anti-c-Myc antibody and Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody as the secondary antibody; binding of the yeast surface displayed domain IIIs to the biotinylated D7 scFv-Fc was detected via PE-conjugated streptavidin. The sorting gate was set to specifically sort out the yeast cells expressing domain III.2 mutants but lacking the binding to biotinylated D7 scFv-Fc. Dramatic enrichment is seen after one round of sorting. (B) Mutated residues derived from the sequence analyses of domain III.2 mutants unable to bind to D7 were shown in red on the crystal structure of DENV envelope protein domain III.2 (PDB code: 2R69), with the original mutation site 310K of the mutant that was used in competitive sorting highlighted in green.