?Mathematical formulae have been encoded as MathML and are displayed in this HTML version using MathJax in order to improve their display. Uncheck the box to turn MathJax off. This feature requires Javascript. Click on a formula to zoom.
?Mathematical formulae have been encoded as MathML and are displayed in this HTML version using MathJax in order to improve their display. Uncheck the box to turn MathJax off. This feature requires Javascript. Click on a formula to zoom.Abstract
This study presents a bibliometric analysis of digital marketing research within small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) spanning from 1985 to 2024. By analyzing 699 publications from the Scopus database, it aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the field’s evolution and current research focuses. The analysis leverages VOSviewer and RStudio’s ‘Biblioshiny’ tools for their robustness in data handling and bias reduction, facilitating a detailed exploration of collaborative networks, key themes and impactful literature. Thematic analysis, enhanced by case studies, identifies emerging areas such as commerce, marketing, digital transformation, costs and Covid-19, offering insights into future research directions. Despite its reliance on Scopus-indexed articles as a limitation, the research contributes to the academic and practical understanding of digital marketing in SMEs, highlighting critical areas for future exploration and development.
1. Introduction
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) play a vital role in economic development, with 80% of global economic growth deriving from them (Amjad, Citation2022; Westgren & Wuebker, Citation2019). However, SME entrepreneurs face various challenges, with marketing being one of the biggest. Indeed, the lack of marketing skills can be a significant barrier to the success of SMEs (Coman et al., Citation2020). With the rise of globalization and the internet, markets have become more open and competitive than ever before.
Digital marketing has become increasingly popular due to the widespread use of the internet and digital devices (Sundaram et al., Citation2020). Digital marketing also allows for more precise measurement of the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, enabling businesses to optimize their strategies and increase their return on investment (ROI) (Robul et al., Citation2020). One of the key aspects of digital marketing is the use of data and analytics to understand consumer behavior and preferences (Bermeo-Giraldo et al., Citation2022; Coman et al., Citation2020). This data can be collected through various digital channels, such as social media, search engines and email marketing campaigns (Choi et al., Citation2016). By analyzing this data, businesses can gain insights into consumer preferences and adjust their marketing strategies accordingly.
Digital marketing also encompasses various other channels and techniques, such as search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, email marketing, social media marketing and mobile marketing (Sundaram et al., Citation2020). Each of these channels has its own unique advantages and requires different strategies and tactics. Overall, digital marketing has revolutionized the way businesses promote their products and services. It offers a wide range of tools and channels for reaching and engaging with consumers, enabling businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers and drive growth and profitability (Amjad, Citation2022; Bermeo-Giraldo et al., Citation2022).
Given the importance of digital marketing in SMEs, we conduct bibliometric analysis to provide a retrospection of the existing literature on this topic. Although there is much research publications about digital marketing in SMEs, a mapping trends of research areas and the future directions seemed needed to be conducted (Amjad, Citation2022; Bermeo-Giraldo et al., Citation2022). Considering the practice of digital marketing continue to evolve over time, this study is trying to fill the gap by aiming to highlight the future direction of research related to digital marketing in SMEs through new perspectives.
In a recent study conducted by Amiri et al. (Citation2023), Fauzi et al. (Citation2023) and Amjad (Citation2022), a bibliometric analysis was undertaken to investigate the landscape of digital marketing practices within small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, this study distinguishes itself from previous research efforts in several significant ways. Primarily, it compiles and presents an exhaustive collection of Scopus-indexed studies pertaining to digital marketing in SMEs, encompassing a total of 699 articles spanning from 1985 to 2024. This study also employs a novel, dual-methodological framework that synergizes the analytical strengths of VOSviewer and RStudio, specifically utilizing the ‘Biblioshiny’ package within RStudio. This innovative approach facilitates a nuanced, dual-faceted examination of the dataset, encompassing both quantitative (through bibliometric analysis) and qualitative (comprehensive literature review) dimensions. This methodology enables a deeper, more comprehensive exploration of the subject matter, thereby contributing a unique perspective to the understanding of digital marketing’s role in the context of SMEs. This research’s novelty lies in its integration of quantitative and qualitative analyses, offering a holistic view of the current landscape and future directions of digital marketing in SMEs. The research questions that are the main focus to be answered in this study include:
RQ1: How has the literature of digital marketing in SMEs developed for the last decades?
RQ2: What are the most contributed authors, organizations and countries in the literature development?
RQ3: What are the important subtopics related to digital marketing in SMEs?
RQ4: What are the future directions of research about digital marketing in SMEs?
This investigation endeavors to enrich the comprehension of digital marketing’s role in SMEs through a methodical and comprehensive analytical process. By scrutinizing an extensive collection of literature on digital marketing spanning more than a decade, this study aims to trace the progression of research within this field and uncover prevailing trends and patterns.
2. Theoretical background
2.1. The concept of digital marketing in SMEs
Digital marketing encompasses the use of digital channels, tools and platforms to promote products or services to a targeted audience, leveraging the internet, social media, email, search engines and mobile apps. In the era of the industrial revolution 4.0, digitization of the economy has brought significant changes in people’s lives globally. The internet has increasingly had a major impact on the ease of doing business activities, from operational processes, marketing to sales (Jones et al., Citation2015). Based on data from the Global Digital Report (Citation2021), the total internet users around the world have reached more than half of the world’s population, which is around 4.66 billion or the equivalent of 59.5% of the total world population, and this number has increased by 7.3% from 2020. The advent of the internet, e-commerce and social media platforms has transformed the way businesses interact with customers and vice versa (Piñeiro-Otero & Martínez-Rolán, Citation2016).
Online shopping has become more accessible and convenient, and people can now access goods and services from anywhere in the world. Digitization has also had a profound impact on the way we work, enabling remote work and collaboration across borders. Online communication tools have made it easier for people to work together, regardless of their location (Jones et al., Citation2015). This has resulted in increased productivity and efficiency for businesses, as well as better work-life balance for employees (Kotler & Keller, Citation2016; Nuseir & Aljumah, Citation2020). Furthermore, digitization has led to the development of new industries and jobs, such as software development, e-commerce and digital marketing.
In the context of SMEs, digital marketing becomes a critical strategy for growth and competitiveness. With limited resources, SMEs prioritize cost-effective and agile digital marketing strategies like social media, email marketing and content marketing to enhance their market presence and drive sales effectively (Bermeo-Giraldo et al., Citation2022; Shideler & Badasyan, Citation2012). However, SMEs lacking in marketing expertise may face challenges in crafting impactful marketing strategies and messages, potentially impeding customer acquisition, revenue generation and sustainable business growth (Amjad, Citation2022; Garo, Citation2017; Westgren & Wuebker, Citation2019). To thrive, SME entrepreneurs must cultivate robust marketing skills, embracing both digital and traditional marketing avenues to deeply understand their target market and competitive landscape (Amjad, Citation2022; Nuseir & Aljumah, Citation2020; Pradhan et al., Citation2020).
Additionally, the complexities of coordinating marketing efforts across different channels and markets can be overwhelming for entrepreneurs with limited resources and experience (Westgren & Wuebker, Citation2019). As a result, it is essential for SME entrepreneurs to develop strong marketing skills and strategies to succeed in today’s global economy. This can include investing in digital marketing techniques, such as social media advertising, search engine optimization and email marketing, as well as traditional marketing tactics like print and television advertising (Nuseir & Aljumah, Citation2020). By developing a deep understanding of their target customers and the competitive landscape, SMEs can create effective marketing campaigns that resonate with their audiences and drive business growth (Amjad, Citation2022; Pradhan et al., Citation2020).
2.2. Comparison of digital marketing between SMEs and large companies
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, the contrast between SMEs and large companies becomes increasingly pronounced (Amjad, Citation2022; Kraus et al., Citation2010; Moriarty et al., Citation2008). This differentiation not only highlights the divergent strategies and resources but also underscores the unique challenges and opportunities each faces in leveraging digital platforms for growth and engagement. provides a comparative summary of digital marketing strategies employed by SMEs and large corporations, underscoring the differences in approach, resources and outcomes between these two business scales.
Table 1. Digital marketing in SMEs and large companies.
shows that digital marketing practices in SMEs contrast significantly with those in large businesses, primarily due to disparities in financial and technical resources, organizational structure and approach to marketing strategies. SMEs often operate with limited budgets, which restricts their ability to adopt advanced marketing technologies (AMTs) and conduct comprehensive market research (Dyerson et al., Citation2016). This leads to marketing strategies that are more tailored, focusing on specific needs and leveraging creativity and entrepreneurial mindsets (Amjad, Citation2022; Mittal et al., Citation2018). For instance, an SME like a local boutique store might rely heavily on social media marketing to connect with its customers. With a limited budget, the boutique could use Instagram and Facebook to showcase new arrivals through posts and stories, relying on the organic reach and personal connections of the owner to spread the word (Rosário & Dias, Citation2023). This approach is direct, cost-effective and leverages the entrepreneurial spirit, focusing on creating personalized experiences for their audience (Rosário & Dias, Citation2023; Yaseen et al., Citation2019).
In contrast, a large multinational company generally uses a wide array of digital marketing strategies that include big-budget ad campaigns across multiple platforms, influencer partnerships and sophisticated data analytics to track consumer behavior and personalize marketing messages (Haenlein et al., Citation2020). Multinational company campaigns are designed to reach a global audience, with the resources to create high-quality content, utilize advanced marketing technologies and conduct extensive market research to inform their strategies (Dost et al., Citation2019; Haenlein et al., Citation2020). While SMEs digital marketing efforts are characterized by personalized, agile and direct engagement with customers, driven by creativity and the personal touch of the business owner, a large multinational company’s approach is more structured, leveraging significant resources for a broad, data-driven marketing strategy (Rosário & Dias, Citation2023).
3. Methodology
3.1. Data
Digital marketing is becoming increasingly important for SMEs as more and more consumers turn to online channels to research and purchase products and services. By conducting a bibliometric analysis of scientific articles related to digital marketing in SMEs that have been published in Scopus-indexed international journals, this study can provide valuable insights into the research trends and patterns in this field. As a data source, Scopus is a reputable and widely-used database that can provide comprehensive coverage of research publications in various fields (Kholidah et al., Citation2022). Overall, this study has the potential to contribute to the understanding of digital marketing in SMEs and provide insights for researchers, practitioners and policymakers interested in this topic.
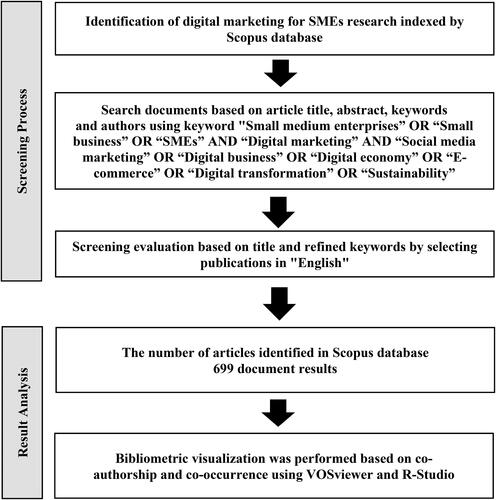
The identification of research publications within the Scopus database was conducted through searches based on various criteria, including subject area or field, author name, publisher, journal, publication year, affiliation, country and keywords. The initial phase of data collection involved the screening of bibliographic documents in Scopus utilizing specific keywords. This process entailed the extraction of research publications from the Scopus database through an advanced search employing the command Article Title-Abstract-Keywords with the terms ‘Small medium enterprises’ OR ‘Small business’ OR ‘SMEs’ AND ‘Digital marketing’ AND ‘Social media marketing’ OR ‘Digital business’ OR ‘Digital economy’ OR ‘E-commerce’ OR ‘Digital transformation’ OR ‘Sustainability’, which yielded 699 publications. The search was executed on 16 February 2024. The following metadata were extracted and compiled into a CSV-formatted corpus file for each publication: author(s), author affiliations, publication title, year of publication, source title, abstract and author keywords. Subsequent refinement of the search results was done based on the ‘English’ language criterion. We have also made an evaluation based on title of publications. Ultimately, 699 scientific articles published over three decades pertaining to digital marketing in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) were identified in the Scopus index. The analysis revealed that research publications on digital marketing within SMEs indexed by Scopus commenced in 1985. The steps of collecting research data is delineated in .
3.2. Method
Bibliometrics employs statistical analysis to scrutinize academic writings, such as articles and books, primarily in library and information science, to track and evaluate scientific research trends and publication patterns (Bellis, Citation2009). This method utilizes statistical and mathematical instruments to dissect written content, charting the evolution of specific academic disciplines (Pritchard, Citation1969). It assesses research fields’ impact and quality by examining citation frequencies, offering insights into prevalent keywords, leading authors and major topics within a research domain. For instance, keyword frequency analysis illuminates core concepts, while author citation frequencies reveal key contributors to a discipline. Such analyses enable an understanding of a field’s structure and growth (Agbo et al., Citation2021; Bellis, Citation2009; Estevão et al., Citation2017; Uluyol et al., Citation2021). The advantage of employing bibliometrics lies in its systematic approach to identify trends, pivotal keywords, leading authors, and core topics that define the evolution of a discipline (Kokol et al., Citation2022). Bibliometrics allowing scholars to efficiently explore academic literature (Agbo et al., Citation2021; Estevão et al., Citation2017; Kokol et al., Citation2022). It highlights key issues, concepts, and methods, revealing current trends and knowledge gaps. This makes bibliometrics essential for guiding scholarly investigation and shaping future research paths (Kokol et al., Citation2022; Tepe et al., Citation2021).
Following the data identification phase, this study progressed to data analysis, employing VOSviewer and RStudio with the ‘Biblioshiny’ package for processing. VOSviewer is renowned for its bibliometric analysis and visualization capabilities, enabling the examination and graphical representation of research networks and citations. It supports the visualization of bibliometric data, facilitating the discovery of clusters or related groups within extensive datasets through methods like co-occurrence, citation and network analysis (Kawuki et al., Citation2021; Nasir et al., Citation2021; Rusydiana, Citation2019; Suban et al., Citation2021; Van Eck & Waltman, Citation2010; Van Eck & Waltman, Citation2014). These techniques help identify research literature patterns, including pivotal keywords and influential authors. VOSviewer’s capability to produce a two-dimensional map showing item similarities enhances understanding of the data’s structure, positioning similar items closely for intuitive analysis (Van Eck & Waltman, Citation2010; Van Eck & Waltman, Citation2014). The following is the VOS equation for mapping the research data (Van Eck & Waltman, Citation2010):
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
Based on EquationEquations (1)(1)
(1) and Equation(2)
(2)
(2) , VOSviewer can generate a two-dimensional map that accurately reflects the similarities between items, with similar items placed closer together and dissimilar items placed farther apart. This map can be a valuable tool for visualizing and exploring the structure of a set of items, such as research articles or keywords in a research field.
In contrast, ‘Biblioshiny’ enhances the analytical process by providing avenues for tailored statistical analyses, advanced clustering techniques and multidimensional scaling (Aria & Cuccurullo, Citation2017). These capabilities enable the identification of subtle and intricate patterns and relationships that may remain concealed when solely relying on network analysis. By employing both tools in concert, this study ensures a more comprehensive and nuanced examination of the SMEs’ digital marketing landscape. Additionally, a case study method is integrated to conduct context analysis on bibliometric findings, enabling a deeper exploration of specific instances and their broader implications in digital marketing. This multifaceted approach not only highlights key trends and patterns but also provides insights into their practical applications, enhancing our understanding of digital marketing’s impact on SMEs. The combination of visual and statistical analyses, along with case study insights, ensures a thorough investigation of emerging themes and the evolving digital marketing field within the context of SMEs.
4. Results and analysis
4.1. Results
4.1.1. Trend of publications
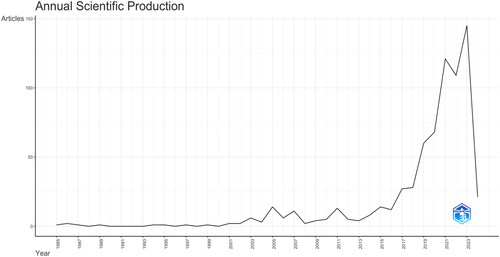
This section aims to address RQ1: How has the literature of digital marketing in SMEs developed over the last decade?. Analyzing the data trends presented in reveals a significant uptick in scholarly interest and research output concerning digital marketing within the SME context. Based on the trend of data, it is clear that the research on digital marketing in SMEs has gained increasing attention over the years, with a noticeable surge in productivity in 2023 which resulted in 145 publications about the topic. This indicates a growing interest among researchers and practitioners in understanding the impact of digital marketing on small and medium-sized enterprises. The fact that this trend has continued into 2024 suggests that there is still much to be learned and discovered about digital marketing in SMEs. It is likely that this research will continue to be an area of focus in the coming years, as the digital landscape continues to evolve and SMEs look for innovative ways to promote their businesses online.
presents the leading journals contributing to research on digital marketing in SMEs, with ‘Sustainability’ and ‘Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems’ each publishing 17 articles, highlighting the sector’s growing research interest. Other significant journals, including ‘Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics’ and ‘Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies’, also focus on this area. These publications are valuable resources for researchers seeking in-depth knowledge and analysis of digital marketing strategies within SMEs. The surge in research productivity related to digital marketing in SMEs is promising, offering insights that can shape strategies for SMEs, policymakers and stakeholders. This body of work deepens our understanding of digital marketing’s challenges and opportunities for SMEs, aiding in the development of more precise and effective support strategies for their digital success. Furthermore, reveals the diverse publication formats for research on SMEs and digital marketing, with scientific articles being the most prevalent, followed by conference papers, reviews, books and book chapters among others.
Table 2. Top five leading journals.
4.1.2. Leading authors, organizations and countries
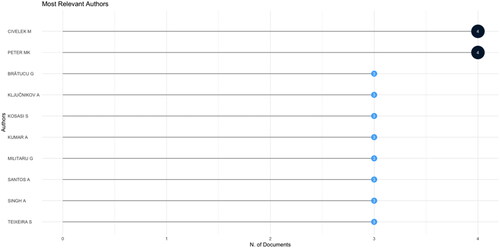
This section seeks to address RQ2 which focus to identify the primary authors, organizations and countries contributing to the literature’s development. Utilizing the Biblioshiny software for initial analysis, the aim was to spotlight the most prominent authors in the realm of digital marketing as it pertains to SMEs. presents the top 10 authors contributing significantly to research in the field of digital marketing for SMEs. Civelek M and Peter MK are ranked as the most relevant authors, each with four publications related to the subject. One notable study by Civelek et al. (Citation2020) investigates the disparities in online marketing and social media tool utilization among Czech, Slovakian and Hungarian SMEs. Meanwhile, a distinguished study by Peter et al. (Citation2020) delves into the strategic action fields of digital transformation, examining the strategic action fields of Swiss SMEs and large enterprises. Each author has provided substantial findings that contribute to the development of related literature.
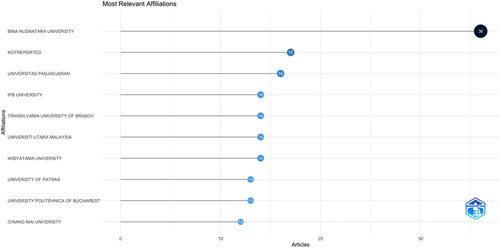
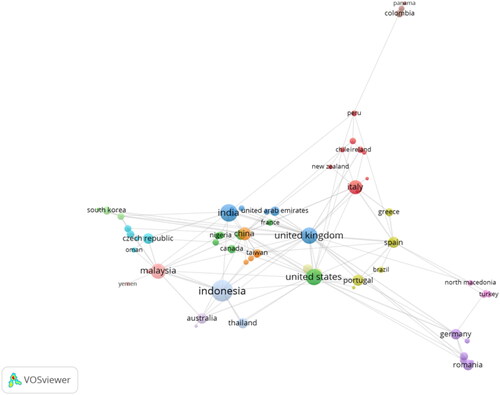
Meanwhile, presents the outcome of an analysis on the most relevant organizations contributing to research on digital marketing within SMEs. It highlights Bina Nusantara University in Indonesia as the leading institution, boasting 36 publications in this area. Consistent with these findings, illustrates the countries that have produced the most research on the topic by VOSviewer, identifying Indonesia as the foremost contributor with a total of 105 articles (). However, when considering the number of citations and total link strength, the United Kingdom emerges as the top-ranked country, followed by the United States, Malaysia, China and Indonesia, making up the top five.
Table 3. Top 10 author’s countries.
4.1.3. Salient keywords, authors keywords and index
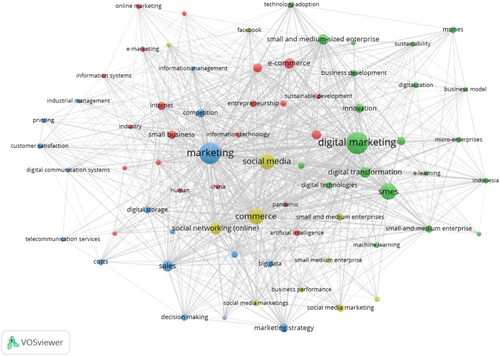
This section endeavors to respond RQ3: What are the important subtopics related to digital marketing in SMEs?. The secondary bibliometric analysis is conducted with the objective of identifying key themes prevalent within the sphere of digital marketing research for SMEs. Utilizing VOSviewer for keyword co-occurrence analysis, this method identifies and visualizes the most common keywords or terms across the literature (). This approach allows for the detection of frequently discussed keywords or themes, offering insights into the main subjects of interest and their interrelations within the field (Kholidah et al., Citation2022).
The keyword co-occurrence analysis entails examining all keywords from each article using VOSviewer, organizing them into clusters based on their occurrence frequency, the interrelations among the terms and the categorization of word clusters. The bibliometric map produced through this analysis is depicted in . Such visualization sheds light on the most recurrent keywords and themes within the SMEs digital marketing literature, elucidating the connections between different topics and themes. The clusters shown are closely related and pertinent to SMEs and digital marketing strategies. Notably, the largest cluster centers around ‘SMEs’ as the key term, encompassing numerous associated keywords like marketing, digital marketing, commerce, SMEs and social media.
Moreover, analyzing the author keywords, which spotlight the terms frequently selected by authors in their abstracts, presents an engaging aspect of the research. This analysis was performed using the ‘Biblioshiny’ tool within RStudio. showcases a bibliometric mapping visualization centered on the primary keywords most commonly used by authors in their abstracts. These keywords serve a dual purpose: enhancing the visibility of research papers in databases through their abstract content and assisting readers in identifying the predominant terms discussed within the studies. Remarkably, among the most utilized keywords, ‘marketing’ represents 15%, ‘commerce’ 9%, ‘digital marketing’ 5% and both ‘social networking (online)’ and ‘sales’ account for 5% each. This alignment of keywords highlights their critical role in the domain of SMEs and digital marketing, emphasizing their significance in grasping the principal themes and focal areas prevalent in academic literature.
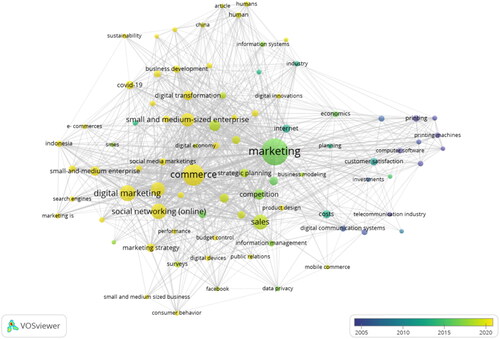
Utilizing unit index analysis and VOSviewer, this study also maps the evolution of digital marketing keywords in SME research, as shown in . Through overlay visualization, which uses color gradients to denote publication years, we trace how research focus shifts over time—from foundational keywords in darker shades representing earlier studies around 2005, to recent themes in lighter shades from 2020 onwards. Central terms like ‘marketing’ and ‘commerce’ have been pivotal, with recent research highlighting ‘digital transformation’, particularly amidst the ‘Covid-19’ pandemic and emerging interests in areas like ‘social networking’, ‘sustainability’ and ‘business development’, indicating a growing emphasis on adapting digital marketing strategies within SMEs.
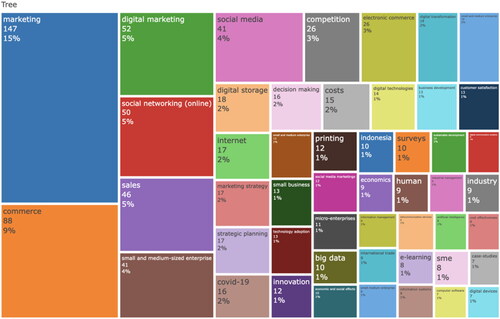
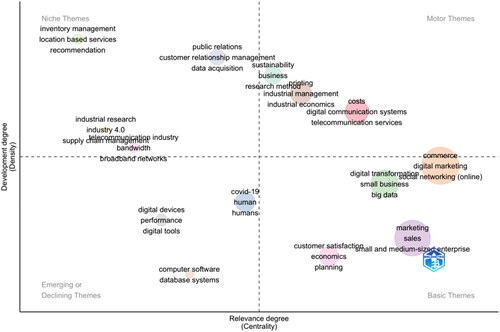
Furthermore, the development of a thematic map, characterized by density and centrality and segmented into four unique topological quadrants as illustrated in , yields additional insights. This result was generated through a semi-automatic algorithm that analyzed the titles and relevant non-author keywords from all references examined in this study. This methodological approach allows for a comprehensive exploration of the underlying themes within the research corpus, facilitating an in-depth understanding of the field’s thematic structure and the interconnectedness of various research topics.
presents a research cluster based on a thematic map derived from a Biblioshiny. It showcases the top five clusters (themes) central to the research field, specifically identified as commerce, marketing, digital transformation, costs and Covid-19. Each theme is broken down into sub-themes, with the table enumerating the occurrences of each sub-theme within the corpus of analyzed literature. This detailed breakdown not only highlights the predominant areas of focus within each cluster but also quantifies the prevalence of each sub-theme, providing a clear view of the landscape and trends in research related to digital marketing in SMEs amidst the Covid-19 pandemic. The sub-themes range from specific marketing strategies and technological innovations to broader societal and economic impacts, reflecting the multifaceted nature of digital marketing’s role and challenges in the contemporary business environment.
Table 4. Top five research cluster based on thematic map.
4.1.4. Trend of publications related to citation
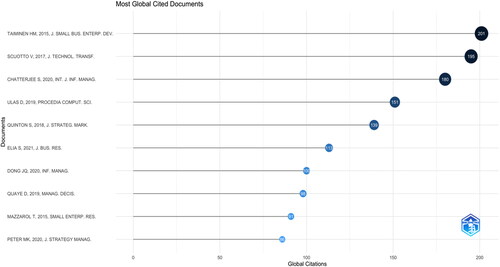
Documented citation analysis constitutes a crucial aspect of bibliometric assessments, offering insights into the most impactful documents within a specific field of study. displays the results from Biblioshiny regarding the most globally cited documents. encapsulates the details of the top five most cited articles globally on digital marketing in SMEs, including the citation count for each article.
Table 5. Top five the most cited articles.
According to , the article by Taiminen and Karjaluoto (Citation2015), titled ‘The usage of digital marketing channels in SMEs’, ranks first with a total of 201 citations. This paper aims to shed light on the employment and objectives of digital marketing, exploring the factors that drive the adoption and usage of digital marketing channels in SMEs. Additionally, other significant contributions to the literature come from articles published by Scuotto et al. (Citation2016), Chatterjee and Kar (2020), Ulaş (Citation2019) and Quinton et al. (Citation2018), each providing substantial insights into the evolving discourse in this domain.
5. Content analysis
This content analysis is grounded in the results obtained from a Thematic Map based on density and centrality, utilizing the Biblioshiny tool (; ). Such an analysis is instrumental in delineating the landscape of current research, pinpointing the central themes and topics that command attention within the scholarly discourse. Focusing on the fields of commerce, marketing, digital transformation, costs and Covid-19, this discussion focuses on the most pertinent themes and articles that align with the top five clusters identified as critical to this research field. This portion is also dedicated to addressing RQ4 to identify the future directions of research about digital marketing in SMEs.
To navigate through this complex terrain, we have distilled the discussion into three pivotal case studies, each reflecting a core aspect of the intersection between digital marketing and SMEs. These case studies include: (1) Digital transformation and e-commerce adoption in SMEs, exploring how small and medium enterprises are navigating the shift toward digital platforms and the implications of e-commerce integration; (2) The impact of digital marketing on SMEs performance, examining the tangible effects digital marketing strategies have on the operational success and growth of SMEs and (3) digital marketing in SMEs during Covid-19, delving into the specific challenges and opportunities presented by the Covid-19 pandemic in the context of digital marketing initiatives within SMEs. Through these focused lenses, we aim to elucidate the dynamic and evolving nature of digital marketing’s role in shaping the future of SMEs.
5.1. Digital transformation and e-commerce adoption in SMEs
In the dynamic landscape of the digital era, SMEs find themselves at a crucial crossroads. The adoption of digital transformation and e-commerce is becoming not just advantageous but essential for their survival and growth. This narrative is supported by an array of research focusing on the transformative impact of digital technologies, particularly social media marketing (SMM), on the business operations of SMEs. These studies collectively highlight the imperative for SMEs to integrate digital strategies to remain competitive and innovative in today’s digital marketplace.
The evolution of digital ecosystems plays a central role in this transformation, as evidenced by the work of Scuotto et al. (Citation2016), who emphasize the potential of social networking sites (SNSs) to drive innovation and improve SMEs’ absorptive capacity and innovation performance. This underscores the importance of online strategies in expanding stakeholder engagement and fostering innovation. Meanwhile, Chatterjee and Kar (2020) point out that factors like perceived usefulness, ease of use and compatibility significantly influence SMM adoption among SMEs, with costs being a notable obstacle. This indicates the necessity for SMEs to find a balance that allows them to fully leverage the benefits of digital marketing tools.
The significance of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and digital platforms in updating SMEs’ operational and marketing strategies is a recurring theme. The research advocates for a deeper investigation into how digital tools can be utilized for growth, with a focus on customer-centric innovation and the strategic application of digital technologies. Ulaş (Citation2019) describes digital transformation as a pivotal phase for redefining traditional business models through digital technologies, essential for enhancing SMEs’ processes and capabilities despite challenges like budget constraints and technological literacy. Similarly, Soroka et al. (Citation2017) discuss the potential of redistributed manufacturing (RdM) to revolutionize small-scale manufacturing, highlighting a research gap in SMEs’ engagement with RdM and big data analytics.
The discussion extends to the adoption of e-commerce in SMEs, revealing complex dynamics that challenge conventional wisdom. Wang et al. (Citation2019) explore the impact of e-commerce on traditional industrial clusters in China, finding that it neither depreciates local production networks nor alters knowledge circulation within clusters. Instead, e-commerce begins to change the inter-dependent relationship between clustering firms and local markets by diversifying marketing channels and enhancing access to individual customers. The Covid-19 pandemic, as studied by Gao et al. (Citation2023), further emphasizes the critical role of e-commerce and digital marketing strategies for MSMEs. Their findings highlight e-commerce as a lifeline for financial sustainability during crises, with digital marketing strategies having a significant impact on financial performance. Adding a unique perspective, Gu (Citation2022) investigates the correlation between CEOs’ prenatal testosterone exposure and e-commerce adoption, suggesting that biological factors may influence the propensity toward embracing digital transformation.
These studies present a holistic view of the e-commerce adoption landscape among SMEs, stressing the importance of a nuanced understanding of digital transformation. They suggest that digital strategies are crucial not just for operational efficiency but for redefining business models, enhancing competitiveness and ensuring sustainability. As SMEs navigate the digital transformation journey, these insights offer valuable guidance for strategic planning and policy formulation, ensuring that SMEs can thrive in the increasingly digitalized global economy.
5.2. The impact of digital marketing on SMEs performance
In an era where digital presence is paramount, SMEs are increasingly leveraging digital marketing to drive growth, enhance customer engagement and improve performance. This evolution is supported by various research findings, demonstrating the diverse impacts and strategic implications of digital marketing on SMEs. We have explored the relevant literatures, which collectively offer insights into the effectiveness of social media, the role of IT resources and the strategic application of digital marketing in enhancing SME performance.
The advent of digital marketing has profoundly impacted the performance of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), offering new avenues for growth, enhanced customer engagement and improved organizational agility. The research conducted by Kosasi et al. (Citation2017) underscores the critical role of digital marketing strategies, particularly through social media, in enhancing the agility of MSMEs by enabling direct access to target markets and fostering innovation. This highlights the opportunity for SMEs to leverage social media technologies for competitive advantage. Wibowo et al. (Citation2020) explore the effective use of social media for digital marketing, emphasizing the importance of understanding big data to create meaningful marketing experiences. Their findings suggest that advertising value and brand awareness, interpreted through big data on social media, significantly influence consumer buying interest, demonstrating the potential of social media to drive purchasing decisions and shape marketing effectiveness.
Ranjan (Citation2023) introduces a conceptual framework to examine the relationship between IT resources and the development of digital marketing capabilities (DMCs), which in turn, enhance business performance. The study reveals that IT advancement and alignment are significant drivers of DMCs, with digital orientation and technological turbulence moderating these effects, indicating the importance of aligning IT resources with digital marketing strategies for improved performance. Meanwhile, Zaitseva et al. (Citation2019) focus on the role of SMM tools in promoting SMEs within the digitalized Russian economy. They argue that effective use of SMM tools not only offers a competitive advantage but also allows for cost-effective marketing compared to traditional methods. Their research emphasizes the importance of SMM in personalizing companies, fostering closer relationships with the target audience and ultimately driving profitability.
Additionally, Sasongko et al. (Citation2023) delve into the impact of digital marketing on the growth of MSMEs, highlighting the significance of various digital marketing instruments in enhancing brand awareness and sales performance. Their findings advocate for the strategic use of digital marketing methods, such as social media advertising and search engine optimization, to foster MSME growth in the digital landscape. Adhitya et al. (Citation2021) examine the role of social media in digital marketing to enhance customer satisfaction and its impact on repurchase intention. Their research demonstrates that brand satisfaction and the effective use of promotions positively influence customer satisfaction, which in turn, boosts repurchase intentions, underscoring the critical role of social media in building customer relationships.
Ravindran et al. (Citation2023) investigate the effects of digital marketing on sales success and enterprise viability, showing a positive correlation between digital marketing and both sales performance and company sustainability. Their study suggests that social media is a key digital platform for SMEs, directly contributing to increased sales volumes. Mohamad et al. (Citation2021) highlight the importance of trust in digital interactive platforms (DIP) for SMEs, pointing out the challenges related to data security and privacy. They propose a model focusing on trust as a moderator for SME internationalization through DIP, indicating the need for secure and transparent digital marketing strategies. Aziz (Citation2022) explores the success factors of international e-commerce among SMEs, identifying digital marketing skills as essential but insufficient on their own. The study emphasizes the need for marketing ambidexterity to maximize the benefits of digital marketing capacities, suggesting a blend of market-driven and market-driving tactics for competitive advantage.
Dallocchio et al. (Citation2024) assess the impact of digital technologies on cross-border e-commerce in Italian SMEs, finding that e-marketing tools significantly influence online export performance. Their research underscores the effectiveness of marketplace presence over proprietary e-commerce websites for SMEs, offering insights for policy makers and managers on leveraging digital technologies for international sales. Octavia et al. (Citation2020) examine the influence of entrepreneurial and market orientation, along with e-commerce adoption, on SME business performance in the digital era. Their findings reveal a significant positive impact of these factors on business performance, stressing the importance of embracing digital e-commerce technologies for market expansion and performance enhancement.
Collectively, these studies illuminate the multifaceted impact of digital marketing on SME performance, highlighting the necessity of integrating digital marketing strategies, aligning IT resources and embracing e-commerce to navigate the competitive digital landscape successfully.
5.3. Digital marketing in SMEs during Covid-19
The Covid-19 pandemic has catalyzed a significant shift in how small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) approach marketing, particularly in terms of digital adoption. This change reflects the necessity to navigate the challenges posed by global lockdowns and social distancing measures, fundamentally altering consumer behavior and market dynamics. The literature explored below provides critical insights into the adaptation and effectiveness of digital marketing strategies among SMEs during this unprecedented period. Ratnasingam et al. (Citation2021) highlight the disruption faced by traditional marketing platforms such as furniture exhibitions and retail outlets due to Covid-19, prompting furniture manufacturers in Malaysia to pivot toward digital marketing. The study reveals an accelerated adoption of digital tools, with larger firms investing more heavily than SMEs, primarily due to financial constraints and a lack of skilled personnel to manage these digital initiatives effectively.
The shift to digital is not confined to any single industry or country. Karjo et al. (Citation2021) detail how household businesses in Jakarta, run by stay-at-home women, successfully utilized social media platforms to maintain sales, emphasizing the crucial role of digital marketing during lockdowns. Similarly, Purnamasari et al. (Citation2023) observe the hurdles and opportunities for MSMEs in Jember Regency, Indonesia, in adopting digital marketing, despite the general lack of familiarity with e-commerce platforms among these businesses.
The agricultural sector, as explored by Haryati (Citation2021) in the context of Indonesia’s mushroom agro-industry, also reveals the potential of digital marketing in creating value and opening up new avenues for business sustainability and growth. Ramadani et al. (Citation2023) further demonstrate how digital marketing and digital transformation positively influence brand promotion and positioning, particularly through the use of social media, across businesses of different sizes in Kosovo. The intent to embrace digital marketing tools in the post-pandemic landscape is highlighted by Müller-Pérez et al. (Citation2022) through their investigation of Tamaulipas MSMEs, applying the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) to understand the factors influencing this adoption. This research, along with the systematic literature review by Hossain et al. (Citation2022), stresses the importance of digital marketing in navigating through crises and enhancing business resilience.
The role of digital marketing in mediating the effects of the pandemic on business performance is explored by Giantari et al. (Citation2022) in Bali’s culinary sector, where its significant influence on non-financial performance is noted. Purba et al. (Citation2021) affirm the substantial impact of digital marketing on the business sustainability and financial performance of Indonesian MSMEs, underscoring the efficacy of digital platforms in ensuring business continuity during challenging times.
Support for local food systems through digital marketing is advocated by Grigorescu et al. (Citation2022), emphasizing the resilience of small farmers in southern Romania and the necessity for digital support to adapt to future shocks. Meanwhile, Giotopoulos et al. (Citation2022) compare the digital development of SMEs and large-sized enterprises in Greece during the pandemic, identifying crucial factors such as investments in ICT and innovative activities that support business digitalization. Lastly, Thaib et al. (Citation2021) examine the influence of organizational policies, company products, marketplace and digital technology on the application of personal selling in the banking sector. The study highlights the significant impact of these factors on achieving company goals, recommending attention to work patterns, reward systems, company reputation, and service quality for optimal results. Collectively, these studies shed light on the transformative role of digital marketing for SMEs during the Covid-19 pandemic, highlighting the necessity for strategic adaptation, investment in digital skills, and leveraging social media and e-commerce platforms to sustain and grow businesses in the face of unprecedented challenges.
6. Conclusion
This bibliometric analysis of digital marketing within small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) identifies significant trends, contributors and thematic focal points in the literature from 1985 to 2024. The study employs a dual-methodological framework, integrating VOSviewer and RStudio’s ‘Biblioshiny’ package, to conduct a detailed exploration of 699 Scopus-indexed articles. This comprehensive approach highlights the increasing scholarly interest in digital marketing for SMEs, with a notable surge in publications in 2023, pointing toward ongoing research momentum in this evolving field. Key contributors identified include prominent authors such as Civelek M and Peter MK and leading institutions like Bina Nusantara University in Indonesia. The research also underscores the significant contributions from countries like United Kingdom, United States, Malaysia, China and Indonesia.
Thematic analysis reveals core areas of interest such as commerce, marketing, digital transformation, costs and the impact of Covid-19 on SMEs. These themes reflect the current research focus and suggest a growing interest in how SMEs can adapt their digital marketing strategies in response to changing technologies and global challenges. Additionally, this study incorporates the case study method as a qualitative inquiry to complement the bibliometric analysis, offering deeper insights into specific instances of digital marketing application within SMEs. This methodological inclusion enriches the research findings, providing contextual examples that illustrate the practical implications of the identified themes and trends. In summarizing, this research provides a holistic view of the digital marketing landscape in SMEs, highlighting the field’s development, key contributors and prevalent themes. By mapping out the research terrain and including case study insights, the study not only charts past scholarly activity but also indicates future directions for research in the domain of digital marketing for SMEs. The study’s implications are significant for both academia, pointing to areas for further exploration and for practitioners, guiding the adoption of effective strategies to boost business performance. It also opens avenues for collaboration and innovation in the digital marketing field.
7. Limitation and future research
As with many studies, this study has two limitations. Firstly, this study is limited to only research publications in the Scopus database. Using only one database such as Scopus can limit the scope of the analysis as several quality publications may not be indexed in Scopus. Combining bibliometric data from Scopus and Web of Science may provide a more comprehensive picture of the research landscape in this field. Furthermore, focusing on high-quality publications listed in databases like the Science Citation Index (SCI), Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) and journals listed in the Australian Business Deans Council (ABDC) can offer a better understanding of the research paradigm from prestigious and influential journals in the field. These databases and journal lists are known for their rigorous selection criteria and are often regarded as indicators of research quality and impact. This can provide more reliable results and can help to identify the most significant contributions in the field of digital marketing in SMEs. These suggestions can be useful for future studies to improve the accuracy and reliability of bibliometric analyses.
This study identifies key future research directions for digital marketing in SMEs, highlighting areas such as essential digital marketing skills, changes in consumer behavior due to Covid-19, cross-cultural strategies, cybersecurity, sustainability and the adoption of technologies like AI and blockchain. These areas offer a roadmap for further exploration into how digital marketing can continue to evolve and support SMEs, providing critical insights for leveraging digital advancements for sustainable business growth.
Author contributions
Nisful Laila: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization.
Puji Sucia Sukmaningrum: Writing – original draft, Validation, Resources, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation.
Wan Azman Saini Wan Ngah: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Formal analysis, Data curation.
Luthfi Nur Rosyidi: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization.
Indah Rahmawati: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization, Conceptualization.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Data availability statement
Raw data were generated from Scopus. Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author (NL) on request.
Additional information
Funding
Notes on contributors
Nisful Laila
Nisful Laila is a distinguished professor in Islamic Finance and Banking and Vice Dean for Resources at the Faculty of Economics and Business, Airlangga University. She obtained Doctoral degree in Islamic Economics from Airlangga University and a Master degree in Banking and Finance from the University of New South Wales. Her research interest is Islamic finance, business management, banking and capital market. She has made numerous contributions to reputable international journals.
Puji Sucia Sukmaningrum
Puji Sucia Sukmaningrum is a lecturer and doctoral candidate in Islamic Economics Program, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga. She has published scientific articles in national and international journals, as well as presented papers at academic conferences in the the areas of Islamic finance and capital markets.
Wan Azman Saini Wan Ngah
Wan Azman Saini Wan Ngah is associate professor of economics at Universiti Putra Malaysia. He obtained PhD from University of Southampton, United Kingdom. His research interest is International finance, Economics and Management. He already published dozen of papers in reputable journals.
Luthfi Nur Rosyidi
Luthfi Nur Rosyidi is a lecturer and doctoral candidate in Islamic Economics Program, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga. His research interests have concentrated on Islamic economics, finance, management and marketing. He has published scientific articles and presented papers at academic conferences in national and international forum.
Indah Rahmawati
Indah Rahmawati is a junior researcher at Islamic Economics Department, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga. She has publication and presented papers at several conferences in Indonesia, Malaysia, Romania and Qatar. She has research interests in the areas of Islamic finance, banking and capital market.
References
- Adhitya, S. B., JanirawantyNst, R., & Yuniarty, Y. (2021 Analysis the role of social media to enhance the effect of service operations and social media review towards customer satisfaction and its impact on repurchase intention on local products of SMEs in Bekasi. In 2021 International Conference on Information Management and Technology (ICIMTech) (Vol. 1, pp. 1–22). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIMTech53080.2021.9535060
- Agbo, J. F., Oyelere, S. S., Suhonen, J., & Tukiainen, M. (2021). Scientific production and thematic breakthroughs in smart learning environments: A bibliometric analysis. Smart Learning Environments, 8(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-020-00145-4
- Amiri, A. M., Kushwaha, B. P., & Singh, R. (2023). Visualisation of global research trends and future research directions of digital marketing in small and medium enterprises using bibliometric analysis. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 30(3), 621–641. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-04-2022-0206
- Amjad, T. (2022). Digital entrepreneurial marketing: A bibliometric analysis reveals an inescapable need of business schools. The International Journal of Management Education., 20(2), 100655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2022.100655
- Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
- Aziz, W. A. (2022). Digital marketing competencies as a factor in the success of e-commerce small businesses in international markets. In 2022 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI) (pp. 402–411). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDABI56818.2022.10041460
- Bellis, N. D. (2009). Bibliometrics and citation analysis: From the science citation index to cybermetrics. Scarecrow Press. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21181
- Bermeo-Giraldo, M. C., Valencia-Arias, A., Ramos de Rosas, J. D., Benjumea-Arias, M., & Villanueva Calderón, J. A. (2022). Factors influencing the use of digital marketing by small and medium-sized enterprises during Covid-19. Informatics, 9(4), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9040086
- Chatterjee, S., & Kar, A. K. (2020, August). Why do small and medium enterprises use social media marketing and what is the impact: Empirical insights from India. International Journal of Information Management, 53, 102103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102103
- Choi, Y.-H., Zaragoza, M. G., Han, D. S., & Kim, H.-K. (2016). Big data and Hadoop for productive social commerce: Trending in social media users and entrepreneurs. International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications, 10(12), 419–430. https://doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2016.10.12.35
- Civelek, M., Gajdka, K., Světlík, J., & Vavrečka, V. (2020). Differences in the usage of online marketing and social media tools: Evidence from Czech, Slovakian and Hungarian SMEs. Equilibrium. Quarterly Journal of Economics and Economic Policy, 15(3), 537–563. https://doi.org/10.24136/eq.2020.024
- Coman, C., Popica, M. M., & Rezeanu, C. (2020). The adoption of digital marketing by SMEs entrepreneurs. In Tatiana Antipova & Álvaro Rocha (Eds.), Digital science, 2019 (pp. 431–441). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37737-3_37
- Dallocchio, M., Lambri, M., Sironi, E., & Teti, E. (2024). The role of digitalization in cross-border e-commerce performance of Italian SMEs. Sustainability, 16(2), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020508
- Digital Report. (2021). Global,Digital 2021: Global Overview Report. Hootsuite (www.hootsuite.com).
- Dost, M., Pahi, M. H., Magsi, H. B., & Umrani, W. A. (2019). Effects of sources of knowledge on frugal innovation: Moderating role of environmental turbulence. Journal of Knowledge Management, 23(7), 1245–1259. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-01-2019-0035
- Dyerson, R., Spinelli, R., & Harindranath, G. (2016). Revisiting IT readiness: An approach for small firms. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 116(3), 546–563. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-05-2015-0204
- Estevão, C., Garcia, A. R., Filipe, S. B., & Fernandes, C. (2017). Convergence in tourism management research: A bibliometric analysis. Tourism & Management Studies, 13(4), 30–42. https://doi.org/10.18089/tms.2017.13404
- Fauzi, M. A., Saad, Z. A., Ahmad, M. H., Fauzi, M. Z., & Ahmad, M. F. (2023). Investigating the emerging and future trends of knowledge management in small and medium enterprises: A science mapping approach. The Learning Organization. Ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/TLO-06-2023-0091
- Gao, J., Siddik, A. B., Khawar Abbas, S., Hamayun, M., Masukujjaman, M., & Alam, S. S. (2023). Impact of e-commerce and digital marketing adoption on the financial and sustainability performance of MSMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic: An empirical study. Sustainability, 15(2), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021594
- Garo, E. (2017). Gap between theory and practice in management education. In Milenko Gudic, Søren Jagd, & Urs Müller (Eds.), Case studies as a teaching tool in management education (pp. 264–277). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-0770-3.ch014
- Giantari, I. G., Yasa, N. N., Suprasto, H. B., & Rahmayanti, P. L. (2022). The role of digital marketing in mediating the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic and the intensity of competition on business performance. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 6(1), 217–232. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2021.9.006
- Giotopoulos, I., Kontolaimou, A., & Tsakanikas, A. (2022). Digital responses of SMEs to the COVID-19 crisis. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 28(7), 1751–1772. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-11-2021-0924
- Global Digital Report. (2021). Digital 2021: Global Overview Report. Hootsuite. www.hootsuite.com.
- Grigorescu, I., Popovici, E.-A., Damian, N., Dumitraşcu, M., Sima, M., Mitrică, B., & Mocanu, I. (2022). The resilience of sub-urban small farming in Bucharest Metropolitan Area in response to the Covid-19 pandemic. Land Use Policy, 122, 106351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106351
- Gu, J. (2022). What drives SMEs to adopt e-commerce? The joint role of testosterone and absorptive capacity. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 35(1), 90–107. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-07-2021-0487
- Haenlein, M., Anadol, E., Farnsworth, T., Hugo, H., Hunichen, J., & Welte, D. (2020). Navigating the new era of influencer marketing: How to be successful on Instagram, TikTok, & Co. California Management Review, 63(1), 5–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/0008125620958166
- Haryati, N. (2021). Business model analysis of mushroom agroindustry and its sustainable development strategy in Covid-19 pandemic. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 733, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/733/1/012125
- Hossain, M. I., Ong, T. S., Tabash, M. I., Siow, M. L., & Said, R. M. (2022). Systematic literature review and future research directions: Drivers of environmental sustainability practices in small and medium-sized enterprises. International Journal of Sustainable Economy, 14(3), 269. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSE.2022.123864
- Jones, N., Borgman, R., & Ulusoy, E. (2015). Impact of social media on small businesses. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 22(4), 611–632. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-09-2013-0133
- Karjo, C. H., Hermawan, F., & Napitupulu, B. E. (2021). The impact of digital marketing media on the household business sales during Covid-19 pandemic. In 2021 3rd International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent System (ICORIS) (pp. 1–4). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICORIS52787.2021.9649491
- Kawuki, J., Ghimire, U., Papabathini, S. S., Obore, N., & Musa, T. H. (2021). A bibliometric analysis of childhood obesity research from China indexed in Web of Science. Journal of Public Health and Emergency, 5, 3–3. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-38380/v1
- Kholidah, H., Hijriah, H. Y., Mawardi, I., Huda, N., Herianingrum, S., & Alkausar, B. (2022). A Bibliometric mapping of peer-to-peer lending research based on economic and business perspective. Heliyon, 8(11), e11512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11512
- Kokol, P., Kokol, M., & Zagoranski, S. (2022). Machine learning on small size samples: A synthetic knowledge synthesis. Science Progress, 105(1), 368504211029777. https://doi.org/10.1177/00368504211029777
- Kosasi, S., Ayu, D., & Yuliani, E. (2017). Improving organizational agility of micro, small, and medium enterprises through digital marketing strategy. In 2017 2nd International Conferences on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE) (pp. 68–72). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITISEE.2017.8285561
- Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2016). Marketing management (15th ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
- Kraus, S., Harms, R., & Fink, M. (2010). Entrepreneurial marketing: Moving beyond marketing in new ventures. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management, 11(1), 19–34. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEIM.2010.029766
- Mittal, S., Khan, M. A., Romero, D., & Wuest, T. (2018). A critical review of smart manufacturing & Industry 4.0 maturity models: Implications for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 49, 194–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.10.005
- Mohamad, A., Mohd Rizal, A., Khalid, H., & Char Fei, T. H. (2021). The role of trust in the digital interactive model for SME speed internationalisation. In 2021 7th International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS) (pp. 1–6). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRIIS53035.2021.9617095
- Moriarty, J., Jones, R., Rowley, J. E., & Kupiec-Teahan, B. (2008). Marketing in small hotels: A qualitative study. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 26(3), 293–315. https://doi.org/10.1108/02634500810871348
- Müller-Pérez, J., Garza-Muñiz, V. S., Acevedo-Duque, Á. E., García-Salirrosas, E. E., Esponda-Pérez, J. A., & Álvarez-Becerra, R. (2022). The future of Tamaulipas MSMEs after COVID-19: Intention to adopt inbound marketing tools. Sustainability, 14(19), 12714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912714
- Nasir, A., Shaukat, K., Iqbal Khan, K., A. Hameed, I., Alam, T., & Luo, S. (2021). Trends and directions of financial technology (fintech) in society and environment: A bibliometric study. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 10353. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110353
- Nuseir, M. T., & Aljumah, A. (2020). The role of digital marketing in business performance with the moderating effect of environment factors among SMEs of UAE. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 11, 310–324.
- Octavia, A., Indrawijaya, S., Sriayudha, Y., H., Hasbullah,., & H., A. (2020). Impact on E-commerce adoption on entrepreneurial orientation and market orientation in business performance of SMEs. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 10(5), 516–525. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.aefr.2020.105.516.525
- Peter, M. K., Kraft, C., & Lindeque, J. P. (2020). Strategic action fields of digital transformation. Journal of Strategy and Management, 13(1), 160–180. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-05-2019-0070
- Piñeiro-Otero, T., & Martínez-Rolán, X. (2016). Understanding digital marketing—Basics and actions. In Carolina Machado & J. Paulo Davim (Eds.), MBA. Management and industrial engineering (pp. 37–74). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28281-7_2
- Pradhan, P., Nigam, D., & Tiwari, C. K. (2020). Partial least square method-structural equation model for assessment of drivers of digital marketing adoption by Indian SMEs. International Journal on Advanced Science, 29, 1286–1296.
- Pritchard, A. (1969). Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. Journal of Documentation, 25, 348.
- Purba, M. I., Simanjutak, D. C., Malau, Y. N., Sholihat, W., & Ahmadi, E. A. (2021). The effect of digital marketing and e-commerce on financial performance and business sustainability of MSMEs during COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 5(3), 275–282. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2021.6.006
- Purnamasari, M., Herdina, A. M., Kumalasari, R. D., Purnama, P. A., & Siregar, N. J. (2023). Implementation of digital marketing in micro, small, and medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in Indonesia during the COVID-19 pandemic. 2023 International Conference On Cyber Management And Engineering (CyMaEn), 88–91.
- Quinton, S., Canhoto, A. I., Molinillo, S., Pera, R., & Budhathoki, T. (2018). Conceptualising a digital orientation: Antecedents of supporting SME performance in the digital economy. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 26(5), 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1080/0965254X.2016.1258004
- Ramadani, V., Istrefi-Jahja, A., Zeqiri, J., & Ribeiro-Soriano, D. E. (2023). COVID-19 and SMEs digital transformation. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 70(8), 2864–2873. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2022.3174628
- Ranjan, P. (2023). IT-related resources, digital marketing capabilities and business performance: Moderating effects of digital orientation and technological turbulence. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 123(11), 2836–2856. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-11-2022-0675
- Ratnasingam, J., Jegathesan, N., Ab Latib, H., Ioras, F., Mariapan, M., & Liat, L. C. (2021). Digital marketing during the COVID-19 pandemic: A case study of its adoption by furniture manufacturers in Malaysia. BioResources, 16(2), 3304–3317. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.16.2.3304-3317
- Ravindran, D., Jaheer Mukthar, K. P., Zarzosa-Marquez, E., Pérez Falcón, J., Jamanca-Anaya, R., & Silva-Gonzales, L. (2023). Impact of digital marketing and IoT tools on MSME’s sales performance and business sustainability. In M. Al Mubarak & A. Hamdan (Eds.), Technological sustainability and business competitive advantage (pp. 65–77). Internet of Things. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35525-7_5
- Robul, Y., Lytovchenko, I., Tchon, L., Nagornyi, Y., Khanova, O., & Omelianenko, O. (2020). Digital marketing tools in the value chain of an innovative product. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 9, 158–165.
- Rosário, A. T., & Dias, J. C. (2023). Marketing strategies on social media platforms. International Journal of E-Business Research, 19(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEBR.316969
- Rusydiana, A. S. (2019). Bibliometric analysis of Scopus-indexed Waqf studies. Ekonomi Islam Indonesia, 1(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.58968/eii.v1i1.1
- Sasongko, A. I., Widjaja, G. C., Theodore, J., Afriliana, N., Matsuo, T., & Gaol, F. L. (2023). The effect of digital marketing on micro, small and medium enterprise in Indonesia. In T. Matsuo, T. Fujimoto, & F. Lumban Gaol (Eds.), Innovations in applied informatics and media engineering. AIMD 2019. Lecture notes in networks and systems (Vol. 677, pp. 147–156). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30769-0_14
- Scuotto, V., Del Giudice, M., & Carayannis, E. G. (2016). The effect of social networking sites and absorptive capacity on SMES’ innovation performance. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 42(2), 409–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9517-0
- Shideler, D., & Badasyan, N. (2012). Broadband impact on small business growth in Kentucky. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 19(4), 589–606. https://doi.org/10.1108/14626001211277415
- Soroka, A.,Liu, Y.,Han, L., &Haleem, M. S. (2017). Big data driven customer insights for SMEs in redistributed manufacturing. Procedia CIRP, 63, 692–697. 10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.319
- Suban, S. A., Madhan, K., & Shagirbasha, S. (2021). A bibliometric analysis of Halal and Islamic tourism. International Hospitality Review, 37(2), 219–242. https://doi.org/10.1108/IHR-05-2021-0038
- Sundaram, R., Sharma, R., & Shakya, A. (2020). Power of digital marketing in building brands: A review of social media advertisement. Journal of International Management, 11, 244–254. 2020
- Taiminen, H., & Karjaluoto, H. (2015). The usage of digital marketing channels in SMEs. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 22(4), 633–651. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-05-2013-0073
- Tepe, G., Geyikci, U. B., & Sancak, F. M. (2021). Fintech companies: A bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Financial Studies, 10(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs10010002
- Thaib, D., Shandra., & S., Widiyanti. (2021). Factors affecting the marketing system of banking for small medium enterprises through the role of agents in the Covid-19 pandemic: A case study. Procedia Environmental Science, Engineering and Management, 9(2), 425–439.
- Ulaş, D. (2019). Digital transformation process and SMEs. Procedia Computer Science, 158, 662–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.101
- Uluyol, B., Secinaro, S., Calandra, D., & Lanzalonga, F. (2021). Mapping Waqf research: A thirty-year bibliometric analysis. Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research, 12(5), 748–767. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIABR-01-2021-0031
- Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
- Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2014). Visualizing bibliometric networks. In Y. Ding, R. Rousseau, & D. Wolfram (Eds.), Measuring scholarly impact: Methods and practice (pp. 285–320). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10377-8_13
- Wang, C. C., Zhang, T., & Song, Z. (2019). E-commerce adoption and the dynamics of the SMEs cluster: Evidence from Zhili children’s garment town, China. China Review, 19, 125–150.
- Westgren, R., & Wuebker, R. (2019). An economic model of strategic entrepreneurship. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 13(4), 507–528. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3581245
- Wibowo, S., Hidayat, R., Suryana, Y., Sari, D., & Kaltum, U. (2020). Measuring the effect of advertising value and brand awareness on purchase intention through the flow experience method on Facebook’s social media marketing big data. In 2020 8th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management (CITSM) (pp. 1–5). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/CITSM50537.2020.9268812
- Yaseen, H., Al-Adwan, A. S., & Al-Madadha, A. (2019). Digital marketing adoption among SMEs in Jordan: A mixed-method approach. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 97(4), 1401–1412.
- Zaitseva, E. A., Srednyak, K. V., & Kudryavtseva, M. (2019). SMM-tools in the promotion of small and medium- sized business (in the case of Nizhny Novgorod market). In 2019 Communication Strategies in Digital Society Workshop (ComSDS) (pp. 93–95). IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMSDS.2019.8709644