Figures & data
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of the Plasmodium falciparum kinome, highlighting kinases that are targets of ongoing drug discovery. Highlighted in blue are the parasite kinases discussed as ongoing targets for drug discovery. The typical protein group families were annotated using Adobe illustrator along with the Aurora kinase family (ARK) and the Apicomplexan-specific kinase family FIKK. Bootstraps values ≥ 30 are represented and annotated on the respective branches; these values relate to the full tree developed using the kinomes of P. falciparum, P. vivax and H. sapiens published in [Citation9,Citation10], which should be consulted for details.
![Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of the Plasmodium falciparum kinome, highlighting kinases that are targets of ongoing drug discovery. Highlighted in blue are the parasite kinases discussed as ongoing targets for drug discovery. The typical protein group families were annotated using Adobe illustrator along with the Aurora kinase family (ARK) and the Apicomplexan-specific kinase family FIKK. Bootstraps values ≥ 30 are represented and annotated on the respective branches; these values relate to the full tree developed using the kinomes of P. falciparum, P. vivax and H. sapiens published in [Citation9,Citation10], which should be consulted for details.](/cms/asset/5a6f1ca0-dc56-4a28-b7f2-abe8c027a3d5/iett_a_2185511_f0001_oc.jpg)
Figure 2. Inhibitors of specific Plasmodium kinases. Indicated below the structures are their IC50 values against the target kinases and their EC50 values against Plasmodium. Unless otherwise stated, EC50 values refer to activity in parasite viability assays in the asexual blood stage.
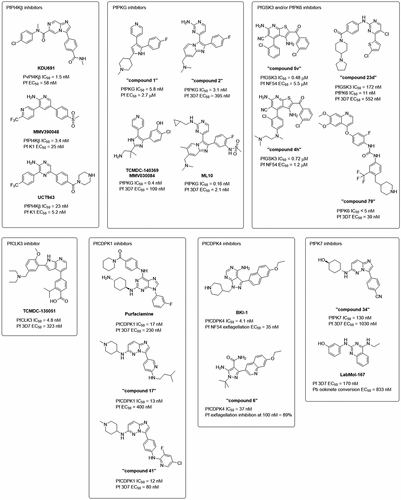
Table 1. Summary of Plasmodium kinase targets discussed, their genetic essentiality to the asexual blood stage of P. falciparum [Citation29,Citation52], biological function, reported inhibitors, availability of commercial screening and crystal structures, and ability to be pulled down from P. falciparum lysate using Kinobeads [Citation14,Citation18–22].
Figure 3. Scaffolds of small molecule kinase inhibitor series with antimalarial activity. Indicated below the structures are their EC50 values determined in asexual blood stage viability assays on various parasite clones.
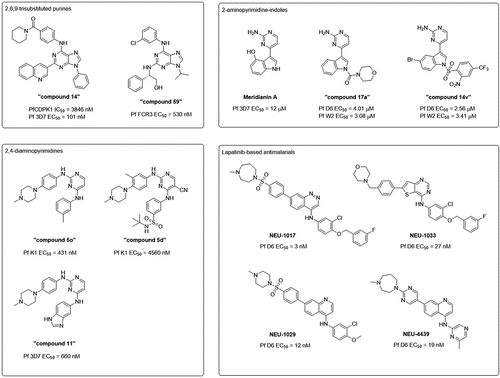
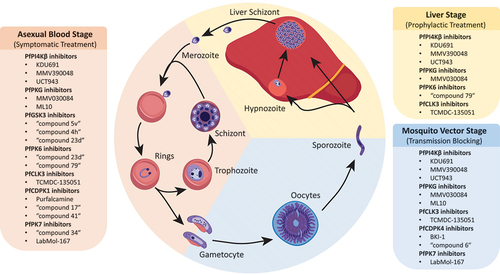
Figure 4. Development stages of the Plasmodium life cycle. Kinase inhibitors that target parasites at the blood, liver and mosquito stages are indicated.