Figures & data
Table 1. The demographics, median ingested dose, Poisoning Severity Score and laboratory findings in patients with metformin only and metformin with other drugs exposures.
Table 2. Most common co-ingested drugs in patients who reportedly ingested metformin with other drugs, for each Poisoning Severity Score.
Figure 1. Median and IQR of ingested dose of metformin for each Poisoning Severity Score in: (a) patients who ingested metformin only (n = 117) and (b) patients who ingested metformin with other drugs (n = 520). *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, and ns: not significant.
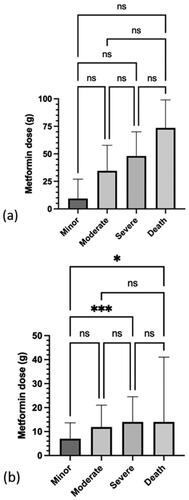
Figure 2. Frequency of the most common clinical features for each Poisoning Severity Score in patients who ingested metformin only (n = 117). Lactic acidosis (metabolic acidosis with arterial pH <7.35 and serum lactate concentration >2.2 mmol/L); abnormal kidney function (serum creatinine >120 μ/L); hypoglycaemia (blood glucose <3.9 mmol/L, 70 mg/dL); hypotension (blood pressure <90/60 mmHg); hyperkalaemia (serum potassium >5.3 mmol/L); acute kidney failure (anuria, serum creatinine >550 μmol/L).
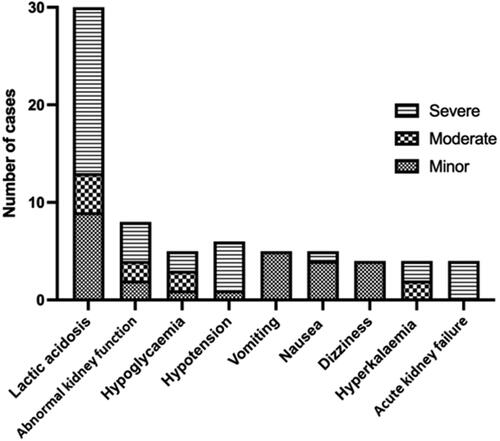
Figure 3. Frequency of the most common clinical features for each Poisoning Severity Score in patients who ingested metformin with other drugs (n = 520). Lactic acidosis (metabolic acidosis with arterial pH <7.35 and serum lactate concentration >2.2 mmol/L); hypotension (blood pressure <90/60 mmHg); somnolence (sedation, drowsiness, sleepiness); tachycardia (heart rate elevated above normal according the age of the patient); coma (unconsciousness); QT prolongation (QTc >450 ms); bradycardia (heart rate <60 beats/minute); hypoglycaemia (blood glucose <3.9 mmol/L, 70 mg/dL).
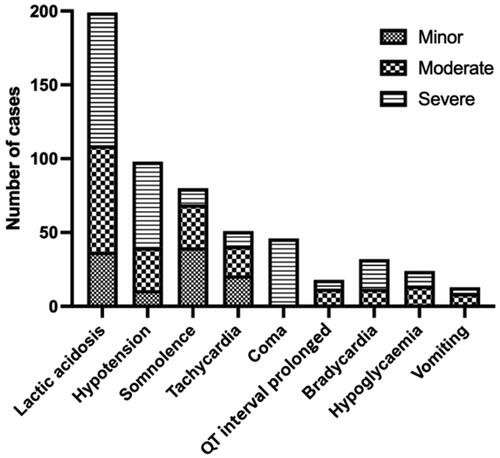
Figure 4. Median and IQR of arterial pH for each Poisoning Severity Score in: (a) patients who ingested metformin only (n = 117) and (b) patients who ingested metformin and other drugs (n = 520). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, and ns: not significant.
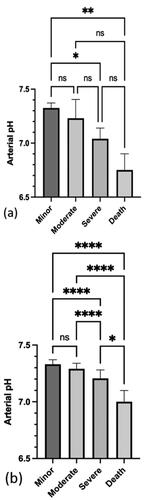
Figure 5. Median and IQR of serum lactate concentration for each Poisoning Severity Score in: (a) patients who ingested metformin only (n = 117) and (b) patients who ingested metformin with other drugs (n = 520). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, and ns: not significant.
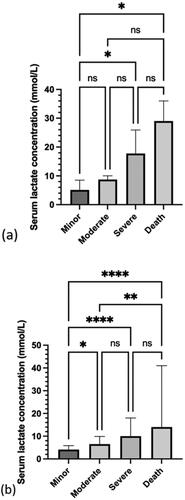
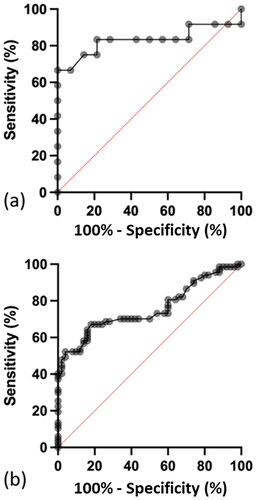
Figure 6. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for serum lactate concentration for a Poisoning Severity Score of minor versus severe in: (a) patients who ingested metformin only. Sensitivity of 75% (95% CI 47–97%) and specificity of 86% (95% CI 60–97%). The optimum serum lactate concentration to distinguish between a minor versus a severe Poisoning Severity Score is 11.0 mmol/L and (b) Patients who ingested metformin with other drugs. The sensitivity was 48% (95% CI 36–60%) and specificity 98% (95% CI 90–100%). The optimum serum lactate concentration to distinguish between a minor versus a severe Poisoning Severity Score is 11.4 mmol/L.