Figures & data
Figure 1. Killing rate of macrophages with different expressions of Dectin-1 to Fonsecaea monophora wild strain (Mel+) or melanin-deficient mutant strain (Mel-). (a) Colony image of surviving F. monophora cultured on PDA for 1 week after 24 h co-culture with macrophages. (b) Killing rate of group (*: P < 0.05).
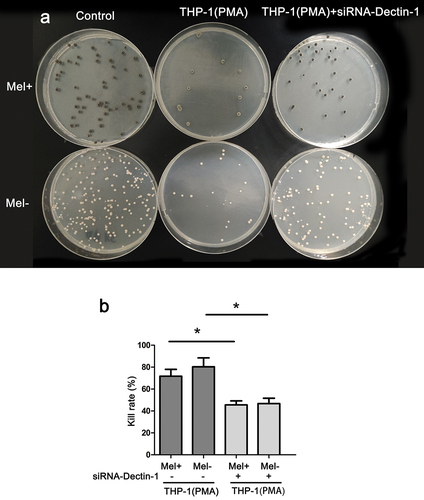
Figure 2. Phagocytic rate of macrophages with different expressions of Dectin-1 to Fonsecaea monophora Mel+ or Mel-. (a) After 4 hours of co-culture with macrophages and F. monophora Mel+ or Mel-, phagocytic image under inverted fluorescence microscopy at a magnification of 200; F. monophora was stained with FITC (green), and macrophage nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (b) Phagocytic rate of each group (**: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001).
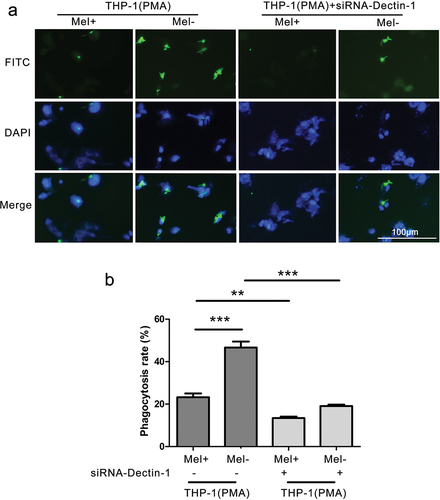
Figure 3. The production proinflammatory cytokines and NO by macrophages with different expressions of Dectin-1 infected by Mel+ and Mel-. after macrophages with different Dectin-1 expression levels were co-cultured with F. monophora Mel+ or Mel- for 24 hours, the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (a), IL-1β (b) and IL-6 (c) in co-cultured supernatants. (d) NO production in each group (*: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001; #: P < 0.05, ##: P < 0.01, ###: P < 0.001).
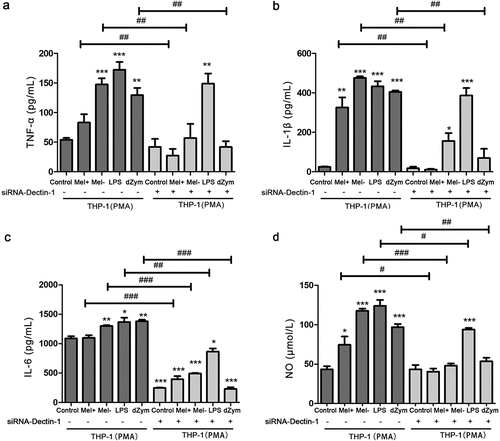
Figure 4. Role of Dectin-1 in immune response of macrophages induced by Fonsecaea monophora Mel+ and Mel-.