Figures & data
Figure 1. Genomic organization and viral particle of ebolaviruses. The single-stranded, negative-sense genome consists of a linear RNA molecule of approximately 19 kb that is composed of seven genes: NP, VP35, VP40, GP, VP30, VP24, and L. The viral particles are filamentous in shape, consisting of a nucleocapsid core surrounded by a viral matrix protein VP40 and a host-derived envelope studded with GP spikes
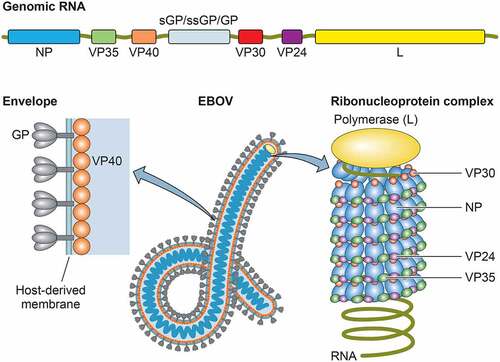
Figure 2. Ebola disease outbreaks and case fatality rates (CFRs) of EBOV, SUDV, and BDBV infections. Forest plot shows the average CFRs and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the Ebola disease outbreaks by fixed-effect model with inverse-variance weighting. Meta-analysis was performed using R software with the metaphor package. The CFRs from the 2013–2016 EVD outbreak caused by EBOV-Makona variant is separately calculated from the average CFRs from all other EVD cases. N.A: not available due to small sample size
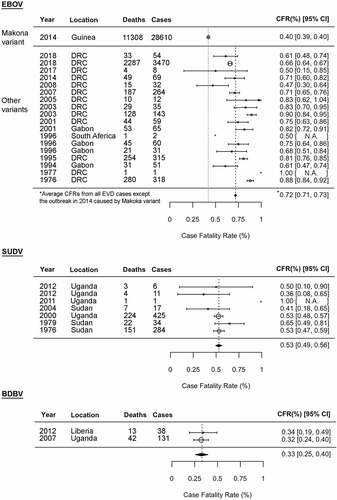
Figure 3. Species-specific and variant-specific virulence of ebolaviruses. Viral ability to spread from macrophages to parenchymal cells, leading to severe organ damage, is one of the key phenotypic features determining ebolavirus pathogenicity. The numbers 1–6 shown in a table on the right are correlated with those shown in a figure on the left. *Including Kupffer cells. na: not available
Table 1. Comparison of fatality rates and time to deaths in animal models infected with different ebolaviruses
Table 2. Comparison of pathogenic functions of viral proteins among ebolaviruses
