Figures & data
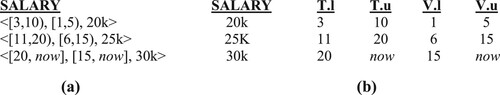
Figure 1. Attribute timestamping. (a) Time points, (b) Intervals, (c) Temporal element, (d) Temporal set.

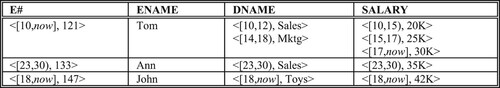
Figure 4. The EMP relation in tuple time stamping. (a) EMP_N Relation, (b) EMP_D Relation, (c) EMP_S Relation.
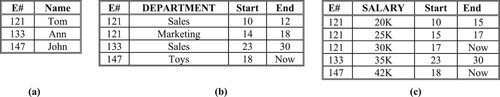
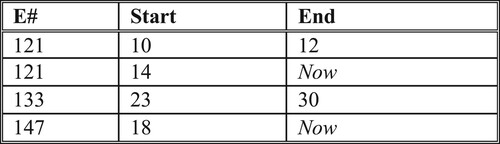
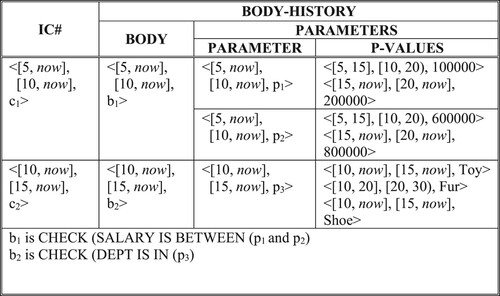
Table 1. Operations for PK and TGI.
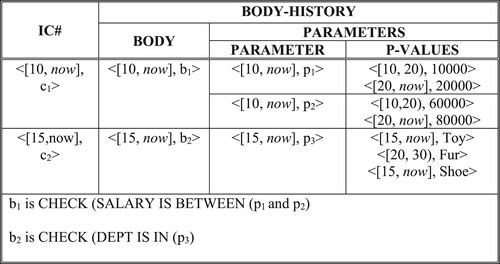
Table 2. Temporal existence integrity constraint.
Table 3. Enforcing time component of temporal existence integrity.
Table
Table
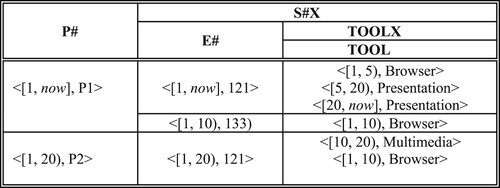
Table 4. Temporal referential integrity constraint.
Table
Table
Figure 11. Department relations in tuple time stamping. (a). DEPARTMENT_LS Relation, (b). DEPARTMENT_B Relation.
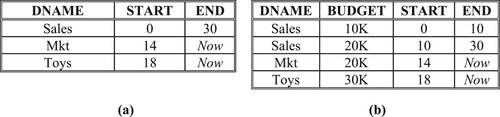
Table 5. Enforcing temporal referential integrity.