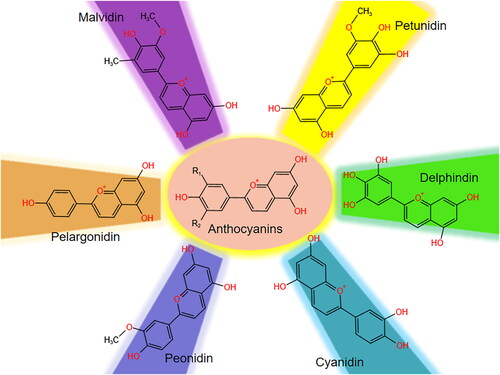
Figures & data
Table 1. the anti-T2DM effect of anthocyanins in clinical trial.
Table 2. Anti-T2DM of anthocyanins in animal trial.
Figure 2. The mechanism of health benefits of anthocyanins on diabetes mellitus and pancreatic islets.
NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-B; cJNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; PC1/3: prohormone convertase 1/3; FoxO1: forkhead box O1; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; GSK3β: Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β; GYS2: Glycogen Synthase 2; G6Pase: glucose 6-phosphatase; PEPCK: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase; CPT-1: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase I; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; SREBP-1: sterol regulatory element binding protein; CYP7A1: Cytochrome P450 Family 7 Subfamily A Member 1; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP: Tissue matrix metalloproteinase; ICAM-1: leukocyte adhesion factors; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; Ngn3: neurogenin3; IRS: insulin receptor substrate; PIK3ca: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PDK1: Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1;
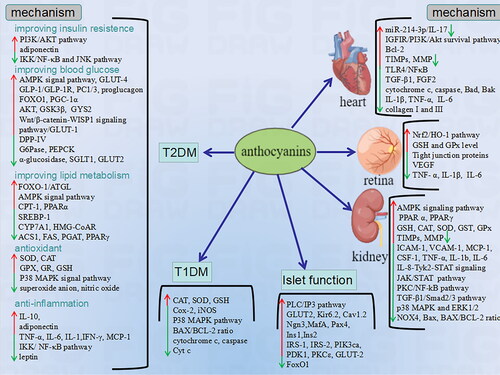
Table 3. The treatment of anthocyanins on diabetic complications in animal trial.
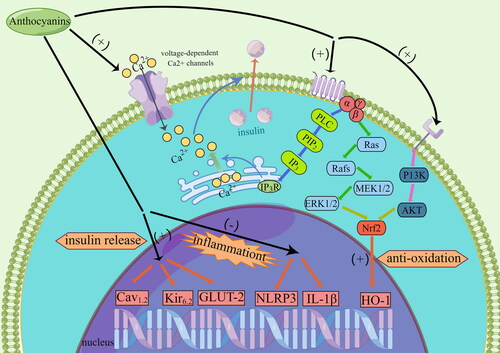
Figure 3. The mechanism of anthocyanins on islets function and transplantation in the cellular level.